What Are Search Engine Algorithms and How Do They Work?
Search engine algorithms are the core systems that decide which pages appear in search results and in what order. These algorithms evaluate billions of documents in milliseconds, interpreting user intent, content relevance, authority, quality signals, and page experience factors to deliver the best possible result for every query.
Unlike early search engines that simply matched keywords, modern search relies on AI-driven semantic understanding, behavior signals, and advanced ranking frameworks. These systems evolve constantly, which means SEO strategies must align with how algorithms interpret quality, trust, intent, and technical performance.
To understand how to succeed in search today, you must understand exactly how search engines crawl, index, and rank the web — and how modern algorithm updates reshape SEO.
How Search Engines Discover and Understand Content?
Search engines begin their work long before a user types a query. The process starts with discovering pages through automated bots.
1. Crawling: How Search Engines Find URLs
Search engines deploy crawlers (also called bots or spiders) that travel from page to page through hyperlinks. These bots follow internal links such as internal links and external links like a backlink to discover new pages.
How deeply a crawler travels on a site depends on your crawl budget, crawl rate, and technical cleanliness, avoiding issues like crawl traps that waste resources.
A well-structured website supported by a logical website structure and descriptive anchor text improves crawl efficiency.
2. Indexing: How Information Is Stored and Interpreted
Once crawled, a page is evaluated and stored in the index. Indexing interprets:
the content’s meaning
metadata
structured data (schema)
media elements (images, videos)
relevance signals
page quality indicators
If your site has issues like duplicate content or incorrectly handled canonical URLs, search engines may choose not to index your page.
Improper configurations can result in de-indexing or index coverage errors, both of which significantly affect visibility.
3. Ranking: How Algorithms Sort Information
When a user performs a query, ranking systems analyze hundreds of signals. These include:
query intent
content relevance
authority
freshness
user experience metrics
semantic understanding
Understanding search intent types and aligning content with the exact intent behind a keyword is now one of the strongest ranking levers.
Pages that satisfy intent and provide deep value stand a better chance of occupying prominent features such as a SERP feature or featured snippet.
The Evolution of Search Engine Algorithms
Search engines have progressed from simplistic keyword-match systems to AI-powered, context-aware ranking ecosystems.
1. Early Ranking Systems: Keywords & Link Authority
The earliest algorithms relied heavily on keyword frequency, which led to manipulative practices such as keyword stuffing.
Google revolutionized search with PageRank, giving weight to backlinks as votes of authority, but this also drove black-hat schemes like link farms and link hoarding.
Today, link-based signals remain important, but Google now evaluates contextual link relevance, making concepts like link equity and link diversity critical.
2. Major Algorithm Updates That Changed SEO
Landscape-shifting updates include:
| Major Update | What It Targeted | SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Panda | Thin or low-quality content | Required content depth + topical authority |
| Penguin | Spammy link building | Prioritized natural, editorially earned links |
| RankBrain | Machine-learning interpretation | Focus on intent, not exact keywords |
| BERT | Understanding natural language | Semantic search optimization |
| Helpful Content Update | Human-first content | Penalizes unhelpful, AI-only output |
Together, these updates made SEO revolve around user satisfaction, semantic relevance, and trustworthy authority, rather than keyword manipulation.
3. The AI Search Era
AI systems like RankBrain, neural matching, MUM, and multimodal models now deeply analyze relationships between words, images, topics, and context.
This means:
synonyms are understood automatically
keyword proximity matters less
topical expertise matters more
search engines interpret meaning, not text density
These advancements reinforce the importance of entity-based SEO, which aligns closely with your terms like Knowledge Graph and topic clusters.
What Search Engine Algorithms Evaluate Today?
Modern ranking systems analyze a vast ecosystem of signals grouped into core categories.
1. Relevance & Query Intent
Modern search engines interpret:
user language
context
situational cues
semantic meaning
This makes keyword research no longer just about volume; understanding keyword intent and avoiding keyword cannibalization is essential.
2. Content Quality & Authority
Google uses multiple layers of evaluation to interpret:
depth of explanation
originality
expertise
accuracy
Authority is influenced by natural links such as an editorial link and branded mentions, along with off-page strategies like outreach marketing.
Pages that offer greater helpfulness and demonstrate expertise tend to rank more consistently, especially when supported by strong content marketing.
3.3 User Behavior & Engagement Signals
While not purely ranking factors, behavior indicators help algorithms infer content usefulness.
Examples include:
interaction patterns
click satisfaction
time spent on page
scroll depth
Optimizing for user experience overlaps with concepts like bounce rate and dwell time.
3.4 Technical Quality & Page Experience
Search engines heavily evaluate:
site speed
mobile usability
security
UX stability
Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and metrics such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) are critical for measuring these factors.
Combined, they contribute to improved crawling, indexing, and ranking.
How Search Engine Algorithms Deliver the Best Result?
Algorithms don’t simply choose the page with the “best content.” They operate in layers:
Ranking Flow Overview Table
| Step | Algorithm Component | What It Evaluates |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Query Understanding | AI interpreters like BERT | Intent, context, meaning |
| 2. Document Matching | Relevance models | Topic alignment, semantic signals |
| 3. Quality Assessment | Core ranking systems | Authority, depth, trustworthiness |
| 4. Page Experience | UX & performance systems | Speed, stability, mobile usability |
| 5. Re-ranking | Personalization & location | Adjusts for user need and environment |
This layered evaluation helps explain why a highly authoritative page may lose rank to a smaller site that better satisfies search intent.
How Algorithms Are Constantly Evolving?
Search engines update their ranking systems thousands of times per year. Many updates are minor, but some reshape SEO entirely.
Updates address:
spam tactics
emerging content formats
new user behavior patterns
better interpretation of quality
These changes mean SEOs must continually adapt — using strategies like content pruning, content freshness optimization, and technical improvements guided by a SEO site audit.
Staying ahead of algorithm shifts requires understanding why algorithms evolve, not just reacting when rankings fluctuate.
What This Means for SEO in 2025 and Beyond?
1. Semantic and Entity-Based Optimization
Instead of chasing keywords, modern SEO focuses on entities, relationships, and topical completeness.
Topical authority improves when your site uses structured clusters, supported by internal links such as:
strategically connected silo structures
natural anchor text relevance
2. Content Must Be Helpful, Not Just Optimized
Google’s Helpful Content System rewards:
human-first material
content written with expertise
answers to real user needs
Thin or outdated information risks becoming thin content, lowering your overall domain trust.
3. Technical Excellence Is Now a Ranking Prerequisite
SEO now requires:
fast rendering
optimized media
clean internal navigation
elimination of broken links
structured data for clarity
As search becomes multimodal and AI-driven, technical alignment is becoming as important as content alignment.
Final Thoughts on how Search Engine Algorithms Truly Work?
Search engine algorithms evaluate hundreds of interconnected signals, powered by AI, semantic understanding, authority frameworks, user-behavior interpretation, and page experience systems.
They no longer reward keyword tricks or surface-level content. Instead, they prioritize:
relevance
user satisfaction
authority
helpfulness
technical stability
Understanding these systems is the foundation of modern SEO. By aligning your content, structure, links, and UX with how algorithms interpret quality, you build long-term, defensible search visibility.
Why Are Search Engine Algorithms Important for Web Rankings?
Search engine algorithms are basically the gatekeepers of the internet. They decide which web pages show up first on search results, making sure you get the most relevant, high-quality, and user-friendly content. Without them? The internet would be a mess—full of random, unreliable, and easily manipulated results.
So, next time you find exactly what you’re looking for on Google, thank the algorithms working behind the scenes!
Key Reasons Why Search Engine Algorithms Matter for Rankings
Search algorithms analyze factors like keywords, links, user engagement, and semantic relevance to match queries with the best content, ensuring users find accurate information quickly.
Filtering Out Low-Quality Content
Algorithms like Google Panda penalize:
- Thin or duplicate content
- Keyword stuffing
- Low-value pages that offer little user benefit
Ranking Based on Authority and Trustworthiness
Search engines prioritize:
- Domain authority – Strength of a website based on backlink profile
- Backlink quality – Trustworthiness and relevance of external links
- Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness – Ensures high-quality, credible content ranks higher
Adapting to User Intent and Search Behavior
AI-driven models like RankBrain, BERT, and MUM help analyze:
- Informational queries – Users looking for knowledge (e.g., “What is SEO?”)
- Navigational queries – Users searching for a specific site (e.g., “Google algorithm updates”)
- Transactional queries – Users looking to make a purchase (e.g., “Buy SEO tools”)
- Commercial investigation – Users comparing options (e.g., “Best SEO software”)
Optimizing for Mobile and Page Experience
Google prioritizes websites with:
- Fast-loading speeds – Affects user experience and rankings
- Mobile-friendly designs – Ensures usability across devices
- Core Web Vitals – Measures page performance, responsiveness, and stability
Preventing Manipulative SEO Practices
Algorithms like Penguin target:
- Link farming and spammy backlinks
- Cloaking and hidden text
- Over-optimized anchor text to manipulate rankings
Improving SERP Features and Enhancing Visibility
Search algorithms determine ranking for:
- Featured Snippets – Quick answers displayed at the top of search results
- People Also Ask (PAA) – Related questions expanding with direct answers
- Knowledge Panels – Fact-based summaries sourced from authoritative sources
- Local Pack Results – Business listings appearing for location-based searches
Search engine algorithms are essential for maintaining fair, relevant, and high-quality search results.
What Are the Core Components of a Search Engine Algorithm?
Think of a search engine algorithm like a well-oiled machine with different parts working together to find and rank the best web pages for your search. It’s built on several key components that help index web pages, rank them accurately, and match them to what users are actually looking for.
Without these pieces working together, search results wouldn’t be nearly as useful or relevant!
1. Crawling
Search engines use bots, known as crawlers or spiders, to discover and scan web pages across the internet. Crawling is the first step in understanding the content of a webpage. Factors that influence crawling include:
- Sitemaps – Help search engines find and understand website structure.
- Internal Linking – Allows bots to navigate between pages efficiently.
- Robots.txt – Directs search bots on which pages to crawl or ignore.
2. Indexing
Once a page is crawled, it is stored in the search engine index, a massive database where web pages are categorized based on content, keywords, and metadata. Important indexing factors include:
- Content Quality – Original, valuable, and well-structured content is prioritized.
- Meta Tags – Title tags and meta descriptions help search engines understand page relevance.
- Canonicalization – Ensures that duplicate content issues don’t affect indexing.
3. Ranking Factors
After indexing, search engines use a ranking algorithm to determine the order of search results. Key ranking factors include:
- Keywords – Matching user queries with relevant content.
- Backlinks – High-quality links from authoritative websites boost rankings.
- User Engagement – Factors like click-through rate (CTR), time on page, and bounce rate influence rankings.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) – Google prioritizes content from credible sources, especially for YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) topics.
4. Query Processing & Search Intent Analysis
Search engines analyze user queries to provide the most accurate and contextually relevant results. Algorithms consider:
- User Intent – Whether a query is informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – AI-powered algorithms like BERT and MUM understand search queries beyond keyword matching.
- Personalization – Search engines tailor results based on location, past search history, and user behavior.
5. AI & Machine Learning in Search
AI-driven algorithms like RankBrain help search engines interpret complex queries, synonyms, and ambiguous search terms. Machine learning also aids in:
- Understanding semantic relationships between words.
- Improving search accuracy based on user interactions.
- Identifying and combating spammy or low-quality content.
6. Search Engine Updates & Algorithm Adjustments
To maintain relevance and combat spam, search engines frequently update their algorithms. Major updates include:
- Google Panda – Targets low-quality, thin content.
- Google Penguin – Penalizes websites using manipulative link-building techniques.
- Google BERT & MUM – Enhances understanding of natural language and context in search queries.
Search engine algorithms rely on crawling, indexing, ranking factors, user intent analysis, AI, and ongoing updates to provide the best search experience.
How Do Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Function in Search Algorithms?
Search engines have a three-step game plan to find and organize web pages: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
First, they crawl the internet, scanning websites for new or updated content. Then, they index what they find, storing it in a massive database. Finally, they rank pages based on relevance, quality, and user intent to decide which results show up first.
Without this process, search engines wouldn’t be able to deliver the right answers when you need them!
Let’s explore each of these steps in detail to gain a clear and comprehensive understanding.
1st:. Crawling: How Search Engines Discover Web Pages
Crawling is the process where search engine bots (also called spiders or crawlers) scan the internet to find new and updated web pages. These bots systematically follow links on web pages to discover new content.
How Crawling Works!
- Search Bots Start with a Known List of URLs – Search engines maintain a list of known websites and discover new ones through sitemaps and backlinks.
- Following Internal & External Links – Crawlers navigate through pages by following links, discovering interconnected web content.
- Respecting Robots.txt Directives – The
robots.txtfile instructs crawlers on which pages they can or cannot visit. - Crawl Budget & Frequency – Search engines allocate a specific crawl budget based on a site’s authority, structure, and update frequency.
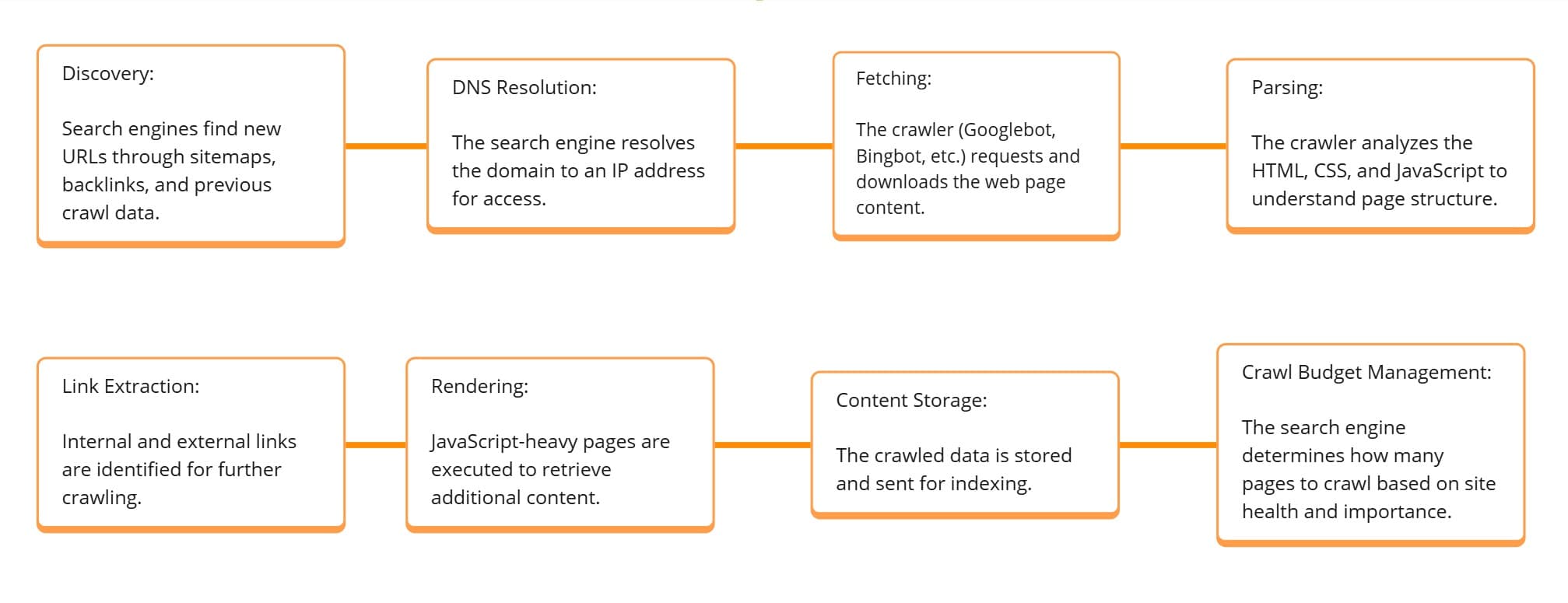
Factors That Affect Crawling Efficiency:
- Sitemaps – XML sitemaps help search engines locate all important pages.
- Internal Linking – A strong internal linking structure allows bots to navigate pages efficiently.
- Page Load Speed – Slow-loading pages may hinder crawling and indexing.
- Blocked Resources – If JavaScript, CSS, or images are blocked, it can impact search visibility.
2nd:. Indexing: How Search Engines Store & Organize Content
After a page is crawled, search engines analyze and store it in a vast database called the search engine index. This index contains billions of web pages, organized based on content, keywords, metadata, and other ranking signals.
How Indexing Works!
- Content Processing – Search engines extract text, images, videos, and structured data from a page.
- Metadata Analysis – Title tags, meta descriptions, and headers help search engines understand page context.
- Duplicate Content Handling – If similar content exists, search engines determine the canonical version to avoid duplicate indexing.
- Mobile-First Indexing – Google primarily indexes and ranks the mobile version of a website.
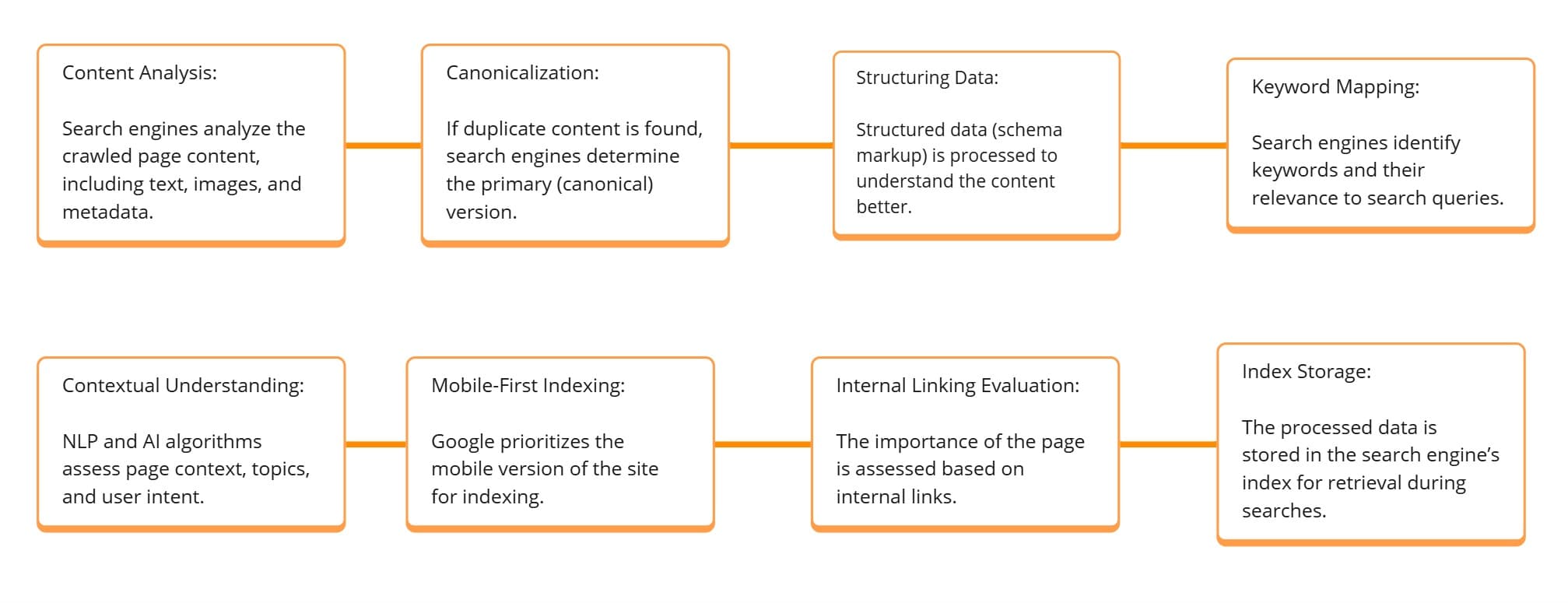
Factors That Affect Indexing:
- Quality Content – Thin, duplicate, or low-quality content may not be indexed.
- Proper Meta Tags – Title tags and descriptions should be clear and keyword-optimized.
- Canonical Tags – Helps search engines avoid duplicate content confusion.
- Mobile Optimization – Mobile-friendly pages are prioritized in indexing.
3rd:. Ranking: How Search Engines Determine Search Results
Ranking is the process of ordering search results based on relevance, authority, and user experience. When a user enters a query, the search engine retrieves relevant indexed pages and ranks them according to a complex set of ranking factors.
How Ranking Works!
- Keyword Relevance – Search engines match a page’s content with the user’s query.
- Authority & Trustworthiness – High-quality backlinks and E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) improve rankings.
- User Engagement Signals – Metrics like click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, and bounce rate influence ranking.
- AI & Semantic Search – Google’s RankBrain, BERT, and MUM help interpret search intent and query meaning.
- Page Experience Signals – Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, and HTTPS security affect rankings.
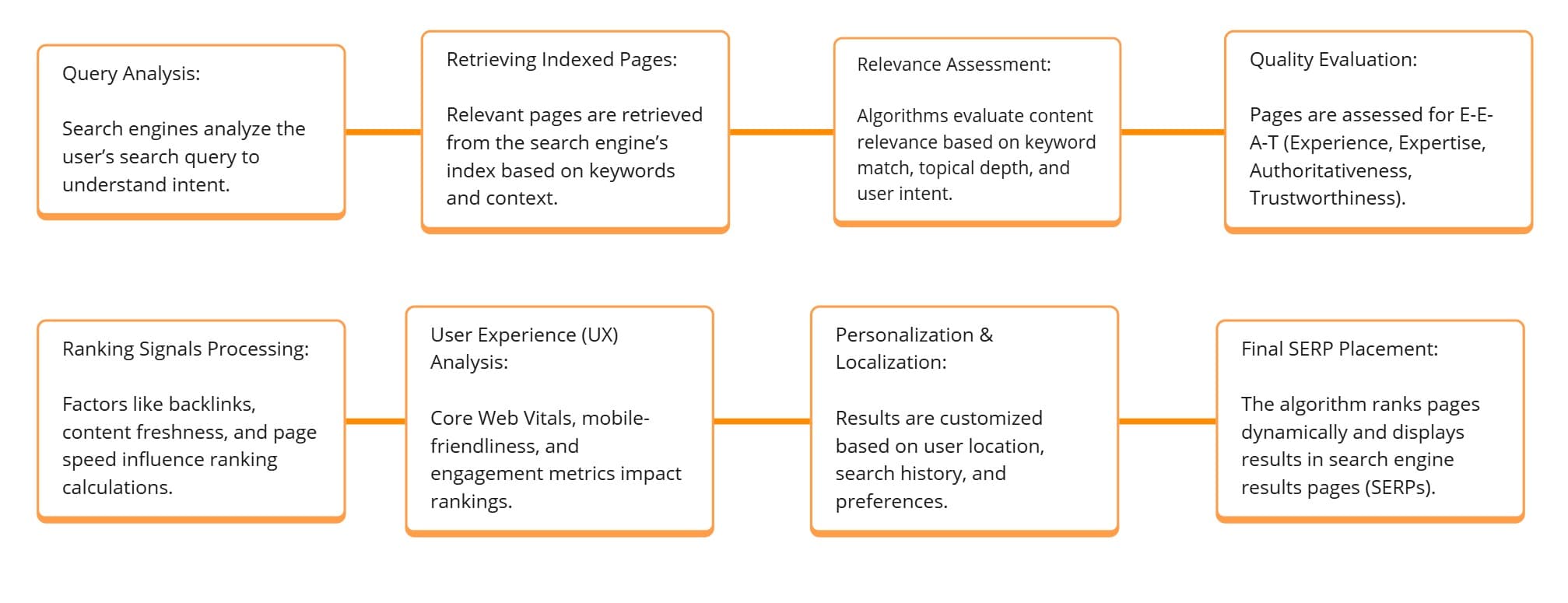
Key Google Algorithm Updates That Influence Ranking:
- Panda – Penalizes low-quality, thin content.
- Penguin – Targets spammy and manipulative link-building tactics.
- RankBrain – Uses AI to refine search intent understanding.
- BERT & MUM – Enhances natural language understanding for complex queries.
Crawling, indexing, and ranking work together to discover, store, and rank web pages in search engines. Websites optimized for efficient crawling, proper indexing, and key ranking factors are more likely to perform well in search results.
What Are the Key Ranking Factors Used by Search Algorithms?
Search engines use hundreds of factors to decide which web pages deserve the top spots in search results.
The exact formula?
That’s Google’s secret sauce.
But SEO experts have cracked the code on some of the biggest ranking signals—things like high-quality content, backlinks, page speed, and user experience. If a website checks all the right boxes, it has a much better shot at ranking higher!
A:. Content Relevance & Quality
Search engines prioritize high-quality, relevant content that aligns with user intent. Key factors include:
- Naturally incorporating primary and long-tail keywords in content, headings, and meta tags.
- In-depth, well-researched articles perform better than thin or generic content.
- Duplicate content is penalized, while original insights and fresh information are rewarded.
- Including images, videos, and infographics improves engagement and ranking potential.
B:. Links, Mentions & Authority (Off-Page SEO)
Backlinks serve as votes of confidence that indicate a page’s credibility. Search engines evaluate:
- Links from authoritative sites (e.g., .gov, .edu, or high-DA domains) carry more weight.
- Backlinks from industry-related sources are more valuable than random links.
- Descriptive anchor text helps search engines understand link context.
- Organic links outperform spammy or paid link schemes (which can trigger penalties).
C:. User Engagement & Experience Signals
Google uses behavioral data to assess how users interact with search results. Important engagement signals include:
- Higher CTR suggests the page is compelling and relevant to users.
- Longer time spent on a page indicates valuable content.
- High bounce rates may signal poor content quality or user experience issues.
If users quickly return to search results after clicking a page, it may indicate irrelevance.
D:. Technical SEO & Page Experience
A well-optimized website with strong technical SEO enhances search rankings. Factors include:
- Google prioritizes pages with fast loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Mobile-first indexing ranks responsive, mobile-optimized sites higher.
- Secure websites with SSL certificates (HTTPS) receive ranking benefits.
- Helps search engines understand page content and enhance rich snippets.
- XML sitemaps, proper robots.txt, and canonical tags prevent indexing issues.
E:. Search Intent & AI-Powered Understanding
Modern algorithms like RankBrain, BERT, and MUM analyze search intent beyond keyword matching. Google categorizes queries into:
- Users seeking knowledge (e.g., “how search engines work”).
- Searching for a specific website (e.g., “Google algorithm updates site:searchenginejournal.com”).
- Ready to take action (e.g., “buy SEO tools online”).
- Comparing options before purchasing (e.g., “best SEO software for ranking analysis”).
F:. On-Page SEO Elements
Optimizing on-page factors helps search engines understand content relevance. Essential elements include:
- Should be compelling, keyword-rich, and within character limits.
- Organize content hierarchically to improve readability and SEO.
- Distributes page authority and guides search bots through site structure.
- Using alt text and compressed images for better accessibility and ranking.
G:. SERP Features & Structured Data
Search algorithms rank content based on how well it fits SERP features, including:
- Answers pulled directly from content, usually ranking in position zero.
- Optimized FAQ content can capture additional rankings.
- Important for businesses targeting geographic locations.
- Optimized multimedia content appears in specialized search results.
H:. Regular Algorithm Updates & SEO Adaptability
Search engines frequently update algorithms to improve search quality. Major updates include:
- Google Panda – Targets thin or low-quality content.
- Google Penguin – Penalizes spammy link-building tactics.
- Google RankBrain – Uses AI to improve query understanding.
- Google Core Updates – Periodic changes that refine ranking criteria.
Websites that adapt to algorithm updates by improving content quality, technical SEO, and user experience gain long-term ranking stability.
Search engines rank web pages based on a combination of content relevance, backlinks, user engagement, technical SEO, and AI-driven search intent analysis.
How Does Google’s Algorithm Differ from Other Search Engines?
Google may be the biggest player in the search game, but it’s not the only one—Bing, DuckDuckGo, and Yahoo all have their own ranking systems too. The goal for all of them is the same: deliver relevant, high-quality results.
But Google stands out because it relies heavily on AI, machine learning, and constant updates to refine search results and stay ahead of the curve.
That’s why Google tends to feel smarter and more intuitive compared to the rest!
1st. Google’s Algorithm
Google’s search algorithm relies heavily on AI, deep learning, and real-time ranking adjustments to deliver highly personalized and intent-driven results.
Key Features of Google’s Algorithm:
- Uses RankBrain, BERT, and MUM to understand complex queries.
- Focuses on context rather than just keywords, improving natural language processing.
- Prioritizes mobile-friendly sites for ranking.
- Measures page speed, interactivity, and visual stability for ranking.
- Releases major updates like Panda, Penguin, and Core Updates to refine ranking criteria.
- Uses past search history and location to tailor search results.
2nd. Bing’s Algorithm
Microsoft Bing’s algorithm differs from Google by placing more emphasis on social media signals and multimedia-rich content.
Key Features of Bing’s Algorithm:
- Bing considers Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn activity as ranking factors.
- Bing rewards high-quality images, videos, and visual search optimization more than Google.
- While backlinks matter, Bing favors older, authoritative domains more than Google does.
- Bing relies more on exact keyword matching than Google’s semantic-based approach.
- Bing provides SEO insights via Bing Webmaster Tools, offering more clarity on ranking factors.
3rd. DuckDuckGo’s Algorithm
DuckDuckGo differentiates itself from Google by prioritizing privacy and unbiased search results.
Key Features of DuckDuckGo’s Algorithm:
- Does not use search history or cookies for personalized results.
- Pulls results from Bing, Yahoo, Wikipedia, and its own crawler.
- Filters out data-tracking and misleading clickbait websites.
- Unlike Google, results are the same for every user.
4th. Yahoo Search
Yahoo Search provides a mix of independent indexing and Bing-powered results, offering a traditional search experience with integrated media and Yahoo-specific content.
Key Features of Yahoo’s Algorithm:
- Uses Bing’s search technology for indexing and ranking web pages.
- Integrates Yahoo’s ecosystem (News, Finance, Sports) into search results.
- Prioritizes multimedia content, making it a strong option for image and video searches.
- Supports paid search advertising through Microsoft’s ad network.
Key Differences Between Google & Other Search Engines
| FEATURE | BING | DUCKDUCKGO | YAHOO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI & Machine Learning | Yes (RankBrain, BERT, MUM) | Limited AI | No AI | Uses Bing’s AI |
| Privacy & Data Tracking | Tracks user data | Tracks user data | No tracking | Tracks user data |
| Mobile-First Indexing | Yes | No | No | No |
| Social Media Signals | No | Yes | No | No |
| Keyword Matching | Semantic & contextual search | More exact-match keywords | Neutral, privacy-focused search | Bing-powered keyword relevance |
| Backlinks & Authority | Prioritizes E-A-T & authority | Prioritizes older domains | Less focus on backlinks | Uses Bing’s ranking model |
| SERP Features | Featured Snippets, PAA, Knowledge Panels | Visual & Video Search | Instant Answers | Yahoo-specific content integration |
Google’s search algorithm remains the most advanced, utilizing AI-driven personalization, semantic search, and continuous updates to refine results. Bing emphasizes multimedia and social media signals, DuckDuckGo focuses on privacy, and Yahoo relies on Bing’s ranking model while integrating Yahoo-specific content and services for a unique search experience.
What Are the Major Google Algorithm Updates and Their Impact?
Google is always tweaking its search algorithm to make results more relevant, user-friendly, and spam-free.
These updates help refine how content is ranked, which means SEO strategies and website rankings are constantly evolving. If a site wants to stay on top, it has to keep up with these changes—because what worked yesterday might not work tomorrow!
1. Google PageRank (1998) – Foundation of Google’s Ranking System
What It Did!
- Introduced link-based ranking, evaluating the quality and quantity of backlinks.
- Pages with more high-authority backlinks ranked higher.
Impact:
- Led to the rise of link-building SEO strategies.
- Later updates (Penguin) penalized manipulative link-building tactics.

2. Google Panda (2011) – Content Quality Update
What It Did!
- Penalized low-quality, thin, and duplicate content.
- Rewarded high-quality, in-depth, and valuable content.
Impact:
- Websites with spammy, copied, or keyword-stuffed content lost rankings.
- Encouraged the adoption of high-quality content strategies.

3. Google Penguin (2012) – Anti-Spam & Link Quality Update
What It Did!
- Targeted spammy backlinks, link farms, and unnatural link-building techniques.
- Devalued paid or manipulated links.
Impact:
- Websites using black-hat SEO tactics saw major ranking drops.
- Boosted importance of natural link-building and content-driven SEO.

4. Google Hummingbird (2013) – Semantic Search & Intent Matching
What It Did!
- Improved understanding of search intent rather than just keyword matching.
- Introduced semantic search, considering synonyms and contextual meaning.
Impact:
- Shifted SEO from exact-match keywords to topic-focused optimization.
- Prioritized conversational search and natural language processing.

5. Google RankBrain (2015) – AI-Powered Search Understanding
What It Did!
- Integrated machine learning (AI) into Google’s ranking system.
- Helped Google process complex queries and understand search intent.
Impact:
- Websites needed better content relevance rather than just keyword optimization.
- User behavior signals (click-through rate, dwell time, bounce rate) became more influential.

6. Google BERT (2019) – Natural Language Processing (NLP) Update
What It Did!
- Enhanced Google’s ability to understand conversational queries.
- Improved context-based results for longer, more complex search queries.
Impact:
- SEO strategies had to focus on contextually rich, well-structured content.
- Benefited long-tail keywords and voice search optimization.

7. Google MUM (2021) – Multimodal & AI Search Evolution
What It Did!
- Used AI to process text, images, and videos together.
- Enabled cross-language search improvements.
Impact:
- Websites with rich multimedia content (images, videos, structured data) performed better.
- Strengthened visual and video search optimization.

Image Credit: licdn.com
8. Google Helpful Content Update (2022) – User-First Content Strategy
What It Did!
- Penalized content written only for SEO (keyword stuffing, AI-generated spam).
- Prioritized helpful, people-first content.
Impact:
- Websites relying on low-value AI-generated content lost rankings.
- Encouraged authentic, in-depth, and user-focused content.

Google Helpful Content Update (2022) Image by earchengineland.com
9. Google Core Updates (Ongoing) – Periodic Ranking Adjustments
What It Does!
- Google frequently rolls out broad core updates to refine ranking criteria.
- Improves search accuracy, spam filtering, and user experience.
Impact:
- Rankings fluctuate periodically, requiring ongoing SEO adjustments.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is a growing ranking factor.
Google’s algorithm updates shape the SEO landscape, favoring high-quality content, user engagement, and natural optimization techniques.
How Do Keyword Searching Algorithms Affect Search Rankings?
Keyword searching algorithms are like the matchmakers of search engines—they help connect users with the most relevant results by understanding what they’re actually looking for. It’s not just about matching words anymore.
Over time, these algorithms have evolved from simple keyword matching to AI-powered semantic analysis, which means search engines can now understand context, intent, and even the deeper meaning behind a query.
Pretty smart, right?
How Search Engines Process Keywords?
When a user enters a query, search engines perform several steps to match the input with relevant content:
- Lexical Analysis – Breaks down the query into individual words and phrases.
- Query Expansion – Uses synonyms, variations, and related terms to widen the search scope.
- Keyword-to-Content Mapping – Matches the query to indexed web pages based on keyword usage, relevance, and search intent.
- Ranking Adjustments – Considers backlinks, user behavior, and AI models to determine final rankings.
Evolution of Keyword Searching Algorithms
A. Exact Match Algorithms (Early Search Engines – 2000s)
How It Worked!
- Ranked pages based on exact keyword matches within content, titles, and metadata.
- More keyword usage led to higher rankings.
Problems:
- Encouraged keyword stuffing and spammy content.
- Lacked understanding of context and search intent.
B. Semantic Search & AI-Powered Algorithms (2013 – Present)
Major Changes:
- Google Hummingbird (2013) – Focused on meaning rather than exact keywords.
- Google RankBrain (2015) – Used AI to process user intent.
- Google BERT (2019) – Improved understanding of natural language and context.
- Google MUM (2021) – Combined text, images, and AI-driven semantic search.
Impact on Keyword Strategies:
- Exact-match keywords are less important than contextual relevance.
- Long-tail keywords perform better due to natural language processing.
- AI interprets synonyms, related topics, and user intent rather than just keyword frequency.
Types of Keyword Searching Algorithms & Their Role!
A. Keyword Matching Algorithms
- Identify exact, partial, and semantic keyword variations.
- Still relevant for title tags, headings, and metadata optimization.
B. Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Algorithms
- Analyze related terms and synonyms to understand content depth.
- Helps rank content based on topic coverage rather than just keywords.
C. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Algorithms
- Used in BERT and MUM updates to improve contextual understanding.
- Essential for voice search and long-form queries.
D. AI & Machine Learning-Based Algorithms
- Google RankBrain adjusts rankings dynamically based on user behavior.
- Search results adapt to click-through rates, dwell time, and search patterns.
How Keywords Influence SERP Features?
Keyword searching algorithms determine eligibility for special SERP features, including:
- Featured Snippets – Answers to question-based queries.
- People Also Ask (PAA) – Variations of the original query based on user interest.
- Auto-Suggestions – Predicts popular search phrases.
- Google’s Knowledge Graph – Displays entity-based results.
Keyword searching algorithms have shifted from exact-match reliance to AI-driven contextual analysis. Today’s SEO strategies must focus on intent, topic depth, and user experience rather than just repeating keywords.
What Role Does AI and Machine Learning Play in Search Algorithms?
Search engines have gotten way smarter, thanks to AI and machine learning. Instead of just matching exact keywords like in the old days, modern search algorithms now understand search intent, user behavior, and content relevance on a much deeper level.
They can process complex queries, natural language, and even context, making search results more accurate and helpful than ever before. It’s like having a search engine that actually gets what you’re looking for!
How AI and Machine Learning Work in Search Algorithms?
AI and ML help search engines analyze massive datasets, recognize patterns, and improve rankings dynamically based on user interactions. These technologies contribute to:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU) – AI models interpret meaning beyond keywords, helping process conversational and voice searches.
- Search Intent Recognition – Algorithms analyze whether a query is informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial.
- Personalized Search Results – AI tailors rankings based on user history, location, and behavior.
- Spam Detection & Content Evaluation – ML identifies and penalizes low-quality, spammy, or AI-generated thin content.
Key AI-Driven Algorithms Used by Google
1st: RankBrain (2015) – AI-Powered Query Understanding
What It Does!
- Uses machine learning to understand search intent and user patterns.
- Adjusts rankings dynamically based on CTR, dwell time, and bounce rate.
Impact on SEO:
- Keyword stuffing became obsolete – Relevance matters more than exact matches.
- User engagement metrics (like time on page) influence rankings.
2nd: BERT (2019) – Contextual & Natural Language Processing (NLP)
What It Does!
- Improves Google’s understanding of conversational search queries.
- Enhances results for long-tail, voice, and complex keyword searches.
Impact on SEO:
- Pages need to focus on natural, well-structured content.
- Question-based and intent-driven queries perform better.
3rd: MUM (2021) – Multimodal AI for Advanced Search Understanding
What It Does!
- Processes text, images, and video simultaneously to enhance search relevance.
- Works across multiple languages, breaking down language barriers.
Impact on SEO:
- Websites with rich multimedia content (videos, images, structured data) perform better.
- Multi-language SEO strategies gain higher visibility.
AI’s Role in Search Engine Ranking Factors
AI helps Google evaluate pages using real-world user engagement rather than just static ranking factors. Key influences include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR) – AI ranks pages higher if they attract more organic clicks.
- Dwell Time & Bounce Rate – If users stay longer on a page, AI assumes it is valuable and relevant.
- Content Freshness & Updates – AI favors sites that regularly update their content.
- Core Web Vitals & UX – AI prioritizes fast-loading, mobile-friendly, and visually stable pages.
AI in Spam Detection & Search Quality Improvements
Search engines use AI models to identify manipulative SEO tactics and low-value content:
- AI-powered spam detection system that fights link spam, cloaking, and keyword manipulation.
- Google AI assesses whether content is written for humans or purely for SEO purposes.
How AI Influences Voice & Conversational Search?
With the rise of voice assistants (Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa), AI helps search engines process:
- AI understands natural language, question-based searches, and voice commands.
- Voice search often includes “near me” queries, enhancing local SEO importance.
AI and Machine Learning have revolutionized search engine algorithms, shifting focus from keywords to intent, context, and user behavior.
Why Do Search Engines Keep Their Algorithms Partially Secret?
Ever wonder why Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo don’t just spill the details on how their ranking algorithms work?
It’s all about fairness, preventing manipulation, and keeping search results high-quality. If everyone knew the exact formula, people would game the system, and search results would be a mess.
Instead, search engines share SEO best practices, but the inner workings of their ranking systems?
That stays under wraps!
1st reason:. Preventing Search Manipulation & Spam
Why It Matters!
If search engines revealed their full ranking criteria, black-hat SEOs would exploit them using keyword stuffing, link farms, cloaking, and content manipulation.
Hidden algorithm details reduce the effectiveness of spam tactics, ensuring genuine, high-quality content ranks higher.
Examples of Algorithm Abuse (Before Google Updates):
- Keyword Stuffing – Early search engines ranked pages based on keyword density, leading to excessive keyword use.
- Link Farms & PBNs – Websites built manipulative backlink networks to artificially boost rankings.
- Hidden Text & Cloaking – Pages displayed different content to search bots vs. real users.
How Search Engines Respond!
Google’s Penguin Update (2012) penalized spammy link-building tactics. Google’s Helpful Content Update (2022) demoted low-quality, AI-generated, and SEO-first content.
2nd reason:. Ensuring Search Quality & Relevance
Why It Matters!
Over-disclosure of algorithms would lead to manipulated rankings where businesses focus on technical optimization rather than genuine user value.
Keeping some aspects secret ensures that authoritative, informative, and trustworthy content ranks higher.
How Search Engines Maintain Quality?
- AI & Machine Learning (RankBrain, BERT, MUM) – Helps interpret user intent beyond keywords.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) – Google prioritizes content from credible sources.
- Spam Detection (SpamBrain) – Uses AI to identify and de-rank manipulative content.
3rd reason:. Preventing Algorithm Gaming by Large Corporations
Why It Matters!
If ranking formulas were public, big companies with high budgets could dominate search results using data-driven SEO hacks, leaving small businesses and new content creators at a disadvantage.
Algorithm secrecy helps level the playing field, allowing quality content to compete against high-budget SEO tactics.
Google’s Efforts to Maintain Fairness:
Core Updates & Algorithm Adjustments – it prevent large sites from monopolizing top rankings. Diversity in Search Results – it ensures multiple websites get visibility rather than just one domain dominating.
4th reason:. Protecting User Data & Personalization Factors
Why It Matters!
Search engines personalize results based on location, browsing history, and user behavior. If algorithms were fully transparent, advertisers and companies could exploit personal data trends to manipulate rankings.
How Google Protects User Privacy?
Privacy-Focused Search (DuckDuckGo, Brave) – Avoids tracking user behavior for ranking. Secure Browsing & HTTPS Prioritization – Enforces safer search experiences.
5th reason:. Keeping Competitive Advantage Over Other Search Engines
Why It Matters!
Google, Bing, and other search engines compete for dominance in the search market. Revealing their full ranking algorithms would allow competitors to replicate their ranking models, reducing Google’s market leadership.
Examples of Competitive Search Features:
- Google Knowledge Graph – Enhances search with direct answers.
- Bing’s Image & Video Search Superiority – Offers better multimedia SERP features.
- Brave & DuckDuckGo’s Privacy-Focused Ranking Models – Cater to privacy-conscious users.
Search engines hide their full algorithms to prevent manipulation, protect search quality, maintain fairness, and safeguard user data.
How Do Search Engine Algorithms Affect SEO and SEM Strategies?
Search engine algorithms are the rulebook for SEO and SEM—they decide which web pages rank where on search results.
As these algorithms keep evolving, businesses can’t just set and forget their strategies.
To stay competitive, they have to constantly tweak and refine their SEO and SEM approaches to keep up with the latest ranking factors. It’s a never-ending game, but keeping up means better visibility and more traffic!
SEO (Optimizing for Organic Search Rankings)
SEO involves improving website visibility in organic (non-paid) search results by aligning with search engine algorithms.
Key SEO Factors Influenced by Algorithms
- Algorithms prioritize natural language and semantic relevance over keyword stuffing.
- Google ranks content with Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T) higher.
- Factors like mobile-friendliness, Core Web Vitals, and HTTPS security affect rankings.
- Search engines favor websites with high-quality, relevant backlinks.
- Click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, and bounce rate impact ranking.
SEO Challenges Due to Algorithm Updates
Google Core Updates cause fluctuations in rankings, requiring SEO professionals to regularly optimize content. Google’s Helpful Content Update penalizes AI-generated or low-value content.
AI-based search (BERT, MUM) makes voice search optimization and contextual relevance more important.
SEM (Paid Advertising & Algorithm Influence)
SEM focuses on paid search strategies such as Google Ads and PPC (Pay-Per-Click) campaigns. While SEM operates differently from organic SEO, algorithms still affect ad placement and performance.
How Algorithms Impact Paid Search Ads?
Google Ads ranks ads based on bid amount, ad quality, and landing page experience.
- More relevant ads get higher Quality Scores, reducing Cost-Per-Click (CPC).
- Google’s AI automates bid adjustments for optimal conversion rates.
- Algorithms personalize ads based on user search history, location, and intent.
SEO vs. SEM: Which is More Affected by Algorithm Updates?
| Factor | SEO (Organic) | SEM (Paid) |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm Sensitivity | High (affected by updates) | Medium (ads adjust dynamically) |
| Traffic Stability | Long-term | Immediate but requires budget |
| Cost | Free (but needs optimization) | Paid (cost varies by competition) |
| Ranking Factors | Content, links, UX | Quality Score, bid, ad relevance |
SEO & SEM Synergy
- SEO Builds Long-Term Authority – Ranking organically boosts credibility.
- SEM Provides Immediate Traffic – Paid ads offer fast visibility & conversions.
- Data from SEM Improves SEO – Paid search data helps identify high-performing keywords for organic content.
Featured Snippets & PAA Optimization – Combining organic and paid search strategies increases SERP dominance.
Search engine algorithms constantly evolve, affecting both SEO and SEM strategies. Successful digital marketing requires staying updated on ranking factors, balancing organic and paid efforts, and optimizing for AI-driven search changes.
What Is the Impact of Algorithm Updates on Website Rankings?
Search engine updates can totally shake up website rankings.
One day you’re on top, and after an update?
You might drop—or jump even higher. These updates are all about rewarding high-quality content and cracking down on shady SEO tricks.
That’s why rankings can fluctuate, and businesses need to stay flexible with their SEO strategies to keep their visibility strong.
Adapt or get left behind!
How Algorithm Updates Influence Rankings?
- Updates like Google Panda prioritize unique, well-structured content while penalizing thin or duplicate content.
- Updates like Google Penguin devalue spammy backlinks, affecting websites that rely on manipulative link-building tactics.
- AI-based updates like RankBrain, BERT, and MUM adjust rankings based on context, intent, and user engagement.
- Updates focusing on Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS security influence rankings.
Common Effects of Major Algorithm Updates
| Algorithm Update | Primary Impact on Rankings |
|---|---|
| Panda (2011) | Penalized low-quality, duplicate, and thin content. |
| Penguin (2012) | Targeted spammy backlink practices and link farms. |
| Hummingbird (2013) | Improved semantic search & intent matching. |
| RankBrain (2015) | Focused on AI-driven ranking adjustments & user behavior. |
| BERT (2019) | Enhanced understanding of natural language & long-tail queries. |
| MUM (2021) | Integrated multimodal search (text, images, video) for better results. |
| Helpful Content Update (2022) | Penalized AI-generated and low-value SEO-first content. |
Why Rankings Drop After Algorithm Updates?
- Pages with thin, irrelevant, or outdated content often lose rankings.
- Excessive keyword use signals spam to search engines.
- Spammy backlinks can trigger penalties under Penguin-like updates.
- Poor site speed, mobile usability, or security can lower rankings.
How to Stay Ahead of Future Algorithm Updates?
- Monitor Google’s Search Central & Industry News – Stay updated with SEO trends and announcements.
- Diversify Traffic Sources – Avoid over-reliance on Google; leverage social media, email, and referral traffic.
- Test & Optimize Content Regularly – Use SEO tools to analyze performance and adapt content accordingly.
Algorithm updates are inevitable and unpredictable, but websites that focus on high-quality content, strong user experience, and ethical SEO will remain competitive.
How Do Search Algorithms Interpret User Intent?
Search engines don’t just look at the words you type—they try to figure out what you actually mean. Thanks to AI, machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP), they can understand user intent, or the reason behind your search.
This helps them deliver results that aren’t just a word-for-word match but actually relevant to what you’re looking for.
Pretty smart, right?
Types of User Intent in Search Algorithms
Search engines classify queries into four main intent categories:
- Informational Intent – The user seeks knowledge or answers (e.g., “How do search engine algorithms work?”).
- Navigational Intent – The user wants to find a specific website (e.g., “Google Search Console login”).
- Transactional Intent – The user is ready to take action, such as purchasing or signing up (e.g., “Buy SEO software online”).
- Commercial Investigation – The user is comparing options before making a decision (e.g., “Best SEO tools for ranking improvement”).
How Search Engines Analyze User Intent?
Search engines do more than just match keywords—they analyze your intent to figure out exactly what you’re looking for.
They break this down using advanced algorithms, AI, and behavioral signals to refine search results.
- It’s not just about exact words—search engines analyze synonyms, related phrases, and context to understand your query.
- Depending on your intent, they might show featured snippets, “People Also Ask” sections, shopping results, or local listings.
- Metrics like click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate, and dwell time tell search engines which results people find useful (and which ones they don’t).
- Technologies like BERT and MUM help search engines process complex, conversational, and even vague queries for more accurate, context-aware results.
Basically, search engines are always learning—so they can deliver what you need, even when you don’t type it perfectly!
Example of Intent-Based Search Algorithm Adjustments
| Search Query | User Intent | SERP Features Displayed |
|---|---|---|
| “What is a search engine algorithm?” | Informational | Featured Snippet, PAA, Knowledge Panel |
| “Google algorithm updates 2025” | Navigational | Google Blog, News Results |
| “Buy SEO software with keyword analysis” | Transactional | Shopping Ads, PPC Ads |
| “Best SEO tools compared” | Commercial Investigation | Product Reviews, Comparison Tables |
How to Optimize Content for Search Intent?
Want your content to rank well?
It’s all about speaking your audience’s language—literally.
Using natural, conversational phrasing and long-tail, question-based queries helps match how real people search.
But it’s not just about keywords.
To really boost visibility:
- If users need a step-by-step guide, give them a how-to article. If they’re comparing products, a detailed comparison works best.
- Structuring content with clear headings, bullet points, and concise answers increases the chances of landing in these prime search spots.
- Search engines now prioritize relevance and value, so whether someone’s looking for info, navigation, a product, or a comparison, your content should deliver exactly what they need.
Do this right, and not only will your rankings improve, but so will engagement and traffic—because your content will be truly useful!
How Do Search Engine Algorithms Influence Search Results?
Search engines don’t just rank content randomly—algorithms decide what shows up and where based on a mix of factors.
Google, for example, goes beyond just keywords. It looks at search intent, structured data, and even user behavior to figure out the best results for each query.
For businesses and content creators, understanding how these algorithms work is key.
The better you align with what search engines prioritize, the more visible and engaging your content becomes. It’s not just about ranking—it’s about making sure your content actually connects with the right audience!
First:. Content Ranking & Featured Snippets
Algorithms like BERT and MUM analyze content relevance to extract concise answers. Structured data and clear formatting improve the chances of appearing in Position Zero results.
Optimization Strategy:
- Use structured headings (H2, H3) and bullet points.
- Provide direct, clear answers within the first 100 words.
- Target question-based queries (e.g., “What is a search engine algorithm?”).
Second:. Semantic Search & People Also Ask (PAA) Expansion
AI models like RankBrain and BERT predict related questions based on user queries. Algorithms dynamically adjust PAA results based on search trends and engagement.
Optimization Strategy:
- Structure content in an FAQ format with concise, direct answers.
- Use question-based subheadings (e.g., “How do search engines rank pages?”).
Third:. Knowledge Graph & Entity Recognition
The Knowledge Graph connects entities using structured data and authoritative sources. Google’s NLP models process relationships between concepts to display fact-based summaries.
Optimization Strategy:
- Use schema markup (structured data) to define brand details.
- Secure citations on trusted sources (e.g., Wikipedia, Wikidata, Google My Business).
Fourth:. Local Search Algorithms & Proximity-Based Rankings
Local rankings depend on proximity, relevance, and prominence factors. Google’s local search algorithm prioritizes businesses with optimized GMB profiles and high engagement.
Optimization Strategy:
- Maintain an accurate Google My Business (GMB) profile with correct NAP (Name, Address, Phone).
- Encourage customer reviews and incorporate localized keywords.
Fifth:. Visual Search & Image Processing (Google Lens & Image Pack)
Google’s MUM AI interprets text and image context to enhance visual search. Image results depend on alt text, metadata, and structured tagging.
Optimization Strategy:
- Use descriptive filenames & alt text with target keywords.
- Optimize images for fast loading speeds and mobile responsiveness.
Sixth:. Video Content & YouTube SEO Algorithms
YouTube’s ranking algorithm prioritizes engagement signals like watch time, clicks, and relevance. Google extracts structured timestamps & transcriptions for video-based search results.
Optimization Strategy:
- Add keyword-rich titles, descriptions, and tags to YouTube videos.
- Include timestamps and transcripts for better indexing.
Seventh:. Product Search & E-Commerce Ranking Algorithms
Google Merchant Center & Shopping Ads algorithms determine product visibility.
Structured product data and user engagement metrics influence ranking in shopping results.
Optimization Strategy:
- Use Google Merchant Center & schema markup for product details.
- Optimize product titles, descriptions, and images for better visibility.
Eighth:. AI-Driven Content Discovery (Google Discover & Personalization)
Google’s AI-powered recommendation systems, including the Google Discover Algorithm, analyze user behavior to suggest content. These algorithms prioritize fresh, engaging, and high-quality content based on user interests, ensuring that users are presented with personalized content tailored to their preferences.
Optimization Strategy:
- Create evergreen & trending content that keeps users engaged.
- Focus on high-quality images, mobile optimization, and structured metadata to improve content visibility.
- Utilize SEO strategies that align with the Google Discover Algorithm’s preferences, including structured data and high-quality visuals, ensuring your content stands out in a personalized feed.
Search engine algorithms, including Google Discover, determine how content ranks and appears in search results. From semantic search and structured data to AI-driven personalization, these systems work together to ensure users receive the most relevant information based on their individual interests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Answers to common questions about search engine algorithms, SEO, and ranking strategies.
What is a search engine algorithm?
A search engine algorithm is a complex set of rules and calculations that search engines use to analyze, rank, and display web pages based on relevance, authority, and user intent.
How do search engine algorithms work?
Search algorithms work by crawling, indexing, and ranking content. They evaluate ranking factors like keywords, backlinks, user engagement, and AI-driven relevance to determine search results.
Why are search engine algorithms important?
Search algorithms ensure users receive relevant, high-quality search results, prevent spam, and help businesses optimize content for better visibility.
What are the different types of search algorithms?
- PageRank – Ranks web pages based on backlinks.
- Semantic Search Algorithms – Understand search intent and context.
- AI & Machine Learning Algorithms – Adapt to user behavior (e.g., RankBrain, BERT, MUM).
What factors influence search engine rankings?
- Content relevance – High-quality, keyword-optimized content.
- Backlinks – Trustworthy and authoritative links.
- User engagement – Click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, and bounce rate.
- Technical SEO – Page speed, mobile-friendliness, and structured data.
What are the major Google algorithm updates?
- Panda (2011) – Penalized low-quality, duplicate content.
- Penguin (2012) – Targeted spammy backlinks and link farms.
- Hummingbird (2013) – Improved search intent matching.
- RankBrain (2015) – Introduced AI to understand complex queries.
- BERT (2019) – Enhanced natural language processing (NLP).
- MUM (2021) – Enabled multimodal search (text, images, and video).
How do Google algorithm updates affect SEO?
Google updates affect SEO by changing ranking factors, penalizing spammy tactics, and prioritizing high-quality content. Websites must adapt by focusing on E-A-T, user experience, and intent-driven content.
How do search engines interpret keywords?
Search engines analyze keyword relevance, semantic meaning, and user intent rather than just exact matches. AI models like RankBrain and BERT improve contextual understanding.
What is the role of AI in search engine algorithms?
AI-powered search algorithms:
- Analyze complex queries and intent (RankBrain).
- Understand natural language and context (BERT, MUM).
- Personalize results based on user behavior.
What are the different types of search intent?
- Informational – Users seek knowledge (“What is a search engine algorithm?”).
- Navigational – Users look for a specific site (“Google algorithm updates 2024”).
- Transactional – Users want to make a purchase (“Buy SEO tools online”).
- Commercial Investigation – Users compare options (“Best SEO software for ranking analysis”).
How does Google personalize search results?
Google personalizes search results based on:
- User location – Local SEO affects rankings.
- Search history – Past searches influence future recommendations.
- Device type – Mobile and desktop results can vary.
How can I optimize my website for search engine algorithms?
To improve rankings:
- Focus on high-quality content (E-A-T).
- Use structured data (Schema Markup) to enhance search visibility.
- Improve Core Web Vitals (site speed, UX, mobile-friendliness).
- Earn authoritative backlinks and engage in ethical link-building.
What’s the difference between SEO and SEM?
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization) – Optimizes for organic rankings.
- SEM (Search Engine Marketing) – Includes paid ads (Google Ads, PPC) to increase visibility.
What are the latest trends in search engine algorithms?
- AI-powered search (Google SGE) – AI-generated summaries may replace traditional rankings.
- Multimodal search (MUM) – Users can search using text, images, and video together.
- Voice search optimization – Conversational queries will dominate.
How will AI change SEO in the future?
AI will impact SEO by:
- Prioritizing user engagement and intent over keyword density.
- Improving personalized search and real-time ranking adjustments.
- Enhancing multimodal and voice search experiences.
How do I rank for featured snippets?
To rank for Featured Snippets:
- Use concise, structured answers (40-60 words).
- Format content with H2/H3 headings, lists, and tables.
- Optimize for question-based queries (Who, What, When, How).
What are Google’s People Also Ask (PAA) boxes?
PAA boxes display related questions with expandable answers. Google selects relevant, high-authority content based on semantic relevance and structured formatting.
Why do rankings drop after an algorithm update?
Rankings may drop due to:
- Low-quality or outdated content.
- Over-optimization (keyword stuffing, unnatural backlinks).
- Slow site speed or poor mobile-friendliness.
- Lack of E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
How can I recover from a Google algorithm penalty?
- Audit content for quality, originality, and depth.
- Improve technical SEO (site speed, UX, and security).
- Earn natural backlinks from trusted sources.
- Optimize for search intent rather than just keywords.
What is semantic search, and how does it affect SEO?
Semantic search helps search engines understand meaning beyond keywords, focusing on search intent, context, and entity relationships. AI models like RankBrain and BERT enhance semantic search.
How does Google’s Core Web Vitals affect rankings?
Core Web Vitals measure:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Page loading time.
- First Input Delay (FID) – Page interactivity speed.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Visual stability.
Sites with poor Core Web Vitals may see ranking drops.
Want to Go Deeper into SEO?
Explore more from my SEO knowledge base:
▪️ SEO & Content Marketing Hub — Learn how content builds authority and visibility
▪️ Search Engine Semantics Hub — A resource on entities, meaning, and search intent
▪️ Join My SEO Academy — Step-by-step guidance for beginners to advanced learners
Whether you’re learning, growing, or scaling, you’ll find everything you need to build real SEO skills.
Feeling stuck with your SEO strategy?
If you’re unclear on next steps, I’m offering a free one-on-one audit session to help and let’s get you moving forward.
Table of Contents
Toggle


