What is Google Ads?
Google Search Ads have become one of the most powerful tools for businesses to connect with high-converting audiences. These text-based ads appear at the top of Google’s search results, triggered by specific keywords that users type in, placing your business right in front of customers who are actively looking for what you offer.
According to Statista, Google accounted for over 83% of the global search ad revenue in 2024, dominating the paid search landscape. Whether you’re a small business owner looking to drive local leads or a digital marketer managing large-scale campaigns, Google Search Ads offer unmatched precision, scalability, and ROI potential.
From targeted keyword bidding to ad extensions that boost visibility, mastering Google Search Ads means unlocking a smarter, more cost-effective way to generate clicks, leads, and sales. In this guide, we’ll break down how it works, why it matters, and how to get the most out of every advertising dollar.
Before going further, let me introduce myself. My name is Nizam Ud Deen, SEO Consultant and Content Marketing Expert. I own an agency called ORM Digital Solutions, where I specialize in Local SEO, Content marketing, and Social Media Strategies. My focus is on providing valuable insights and helping businesses grow online.
Example of a Google Ad on Mobile
This is a Google Search Ad displayed on a mobile device. It features a “Sponsored” label at the top, clearly indicating that it’s a paid placement rather than an organic result. A globe icon appears next to the display URL (balmysunhotel.com), signifying that this is an ad served from a verified website. The ad includes a headline with a strong call to action (“Book Direct”) and a short description that highlights the unique selling points of the business—luxury, beachfront access, and memorable experiences.
Theoretical Research on Google Ads!
Google Ads is a pay-per-click (PPC) advertising platform that allows businesses, agencies, marketers, and even freelancers to create highly targeted text-based ads displayed on Google Search results and Google Search Partner websites. It is designed to capture high-intent audiences actively searching for products, services, or information, making it one of the most effective tools to drive traffic, generate leads, and boost sales. Ads operate on a cost-per-click (CPC) or cost-per-impression (CPM) model, ensuring businesses pay only when users interact with their ads. With ad placements appearing prominently at the top and bottom of search results, advertisers can ensure maximum visibility for their campaigns, leveraging campaign types such as standard search ads, dynamic search ads (automatically matching ads to search queries using website content), responsive search ads (AI-driven ad optimization), and call-only ads (focused on driving direct phone calls). For broader goals, options like Performance Max Campaigns, Shopping Ads, and Local Ads expand reach across platforms like YouTube, Gmail, and Discover.
The platform offers robust targeting options, including keyword targeting (broad, phrase, and exact match), in-market audiences (users actively researching products/services), affinity audiences (long-term interests such as “Tech Enthusiasts“), customer match (uploading contact lists for retargeting), geographical targeting (from hyperlocal zip codes to global audiences), and demographic segmentation based on age, gender, income, and even parental or marital status. Advertisers can also leverage lookalike audiences to target users with similar characteristics to existing customers, ensuring highly optimized spending. Campaigns can be customized with tailored ad copy, display URLs, and a wide variety of extensions, including sitelink extensions, callout extensions, structured snippets, and image extensions that make ads more engaging and actionable.
With advanced features like AI-powered bidding strategies such as Target CPA, ROAS, and Maximize Conversions, Google Ads automates optimization to achieve specific goals efficiently. Tools like Keyword Planner, Auction Insights, and Conversion Tracking help advertisers refine their campaigns and measure results effectively, while integrations with Google Analytics 4 (GA4), Google Tag Manager, and third-party CRMs like HubSpot or Salesforce provide deeper insights and streamlined workflows. Performance metrics such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, cost-per-conversion, and return on ad spend (ROAS) are readily available, helping businesses track their success and refine strategies in real time.
Google Ads Search Advertising caters to diverse industries, including e-commerce, where Shopping Ads drive online sales; local businesses, which can benefit from Local Ads; startups, aiming to boost brand visibility; B2B services, which focus on high-value leads; and the hospitality industry, which uses regional targeting to increase bookings. With no fixed minimum budget, campaigns can be scaled according to business needs, while the ad auction system, determined by Ad Rank (a combination of Quality Score and CPC Bid), ensures cost-efficiency and competitive placements. Advertisers can adjust budgets in real time, making it flexible and accessible for businesses of all sizes.
While Google Ads Search Advertising offers significant advantages, challenges such as high competition in certain industries (leading to higher CPCs), the steep learning curve for new users, and ad fatigue (requiring regular updates to ad copy) must be addressed. Emerging trends like voice search optimization, privacy sandbox compliance for a cookieless future, and sustainability metrics showcase the platform’s adaptability to changing advertising landscapes. Google provides extensive support through resources like Google Skillshop (certifications and training), direct customer support via chat or phone, and integrations like AdSense for publishers monetizing their sites.
Google Ads Search Advertising distinguishes itself from competitors like Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads), Amazon Advertising, and TikTok Ads by focusing on high-intent users and offering unmatched customization, targeting, and analytics features. Whether you are a local business, an e-commerce brand, or a global enterprise, Google Ads Search Advertising enables campaigns to be tailored for success, leveraging its extensive ecosystem and tools to maximize results and engage the right audience at the right time.
How to Create Google Ads Account?
Creating a Google Ads account is the first step toward launching your paid search campaigns. Whether you’re a small business owner or a digital marketer, this process is beginner-friendly and only takes a few minutes.
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
What Do I Need Before Creating a Google Ads Account?
Before you begin setting up your Google Ads account, gather the following essentials to ensure a smooth registration process and avoid interruptions later:
1. A Google Account (Gmail)
You must have an active Google account to use Google Ads. This will be your login and admin account.
If you’re running ads for a business, use a company email tied to a Google Workspace account.
If you’re managing ads for clients, consider using a separate Gmail account to keep access organized.
2. Your Business Website URL (Optional but Recommended)
While not mandatory, having a website helps:
Improve your ad credibility — users expect to land on a legit site.
Unlock full features — like conversion tracking, landing page experience score, and remarketing.
Control destination — your ad’s final URL should match your landing page’s content for better Quality Score.
Note: If you don’t have a website, you can still run ads that direct users to call your business or visit a physical location using Smart Campaigns.
3. A Valid Payment Method
To run any ads, you must enter billing details. Supported methods include:
Credit cards (Visa, Mastercard, American Express)
Debit cards (must be international use-enabled)
Bank transfer/direct debit (depending on your country)
PayPal (available in select regions)
Make sure your payment method has sufficient funds to avoid ad pauses due to billing failures.
Tip: You can choose between automatic payments (billed after clicks) or manual payments (prepay before running ads), depending on availability in your region.
How Do I Start the Google Ads Sign-Up Process?
The Google Ads sign-up process is quick but requires precision, especially if you’re aiming for full control over your ad campaigns. Follow these exact steps:
Step 1: Visit the Official Google Ads Website
Go to https://ads.google.com using a desktop or mobile browser.
Preferably use a desktop for full access to advanced features.
Make sure you’re using a secure connection (look for the padlock icon in the address bar).
Step 2: Click the “Start Now” Button
On the homepage, you’ll see a blue “Start now” button in the top-right corner.
Clicking this will redirect you to the Google Ads onboarding page.
If you’re already logged into a Google account, it’ll take you straight to the setup flow.
Step 3: Sign in or Create a Google Account
You’ll be prompted to sign in using your existing Google (Gmail) account.
If you already use Google services like Gmail, YouTube, or Google Drive, use the same login.
If you’re managing ads for someone else (like a client), consider creating a dedicated Google Ads login to keep accounts separate and manageable.
Important: The account you use here will become the primary admin of the Google Ads account. While you can add users later, the email used during sign-up will retain full control unless changed manually.
What Happens Next?
Once you’re logged in, you’ll be taken to the campaign setup page, where Google tries to walk you through creating your first Smart Campaign. If you’re looking for more control:
Scroll down and click “Switch to Expert Mode” — this allows you to skip campaign creation and go straight to your full dashboard.
What’s the First Thing Google Ads Asks Me to Do?
When you begin the Google Ads setup process, Google immediately guides you into creating your first ad campaign — but the path you choose here defines how much control you’ll have over your account from the start.
Google Defaults to “Smart Campaign” Setup
Right after signing in, Google shows a simplified workflow where you’re prompted to:
Select your advertising goal (e.g., get more calls, website visits, or physical store visits).
Enter your business name and website URL.
Let Google auto-generate a basic ad based on limited info.
This flow is part of Smart Campaigns, designed for beginners and local businesses. It automates much of the setup, including targeting, bidding, and keywords.
Pros of Smart Campaigns:
Fast and beginner-friendly
Google handles most decisions
Great for basic lead generation
Cons:
Limited control over keyword targeting, bidding strategies, ad placements
Less transparency in campaign performance metrics
No access to advanced features like ad scheduling, extensions, or conversion tracking
Want Full Control? Switch to “Expert Mode”
At the bottom of the Smart Campaign screen, you’ll see a small link:
🡒 “Switch to Expert Mode”
Clicking this does the following:
Gives you access to full Google Ads features, including campaign types (Search, Display, Video, Performance Max, etc.).
Lets you manually configure settings like bidding strategies, keyword match types, ad groups, targeting, and more.
Offers complete customization, better for experienced advertisers or those working with marketing agencies.
Tip: Even if you’re a beginner, it’s often better to switch to Expert Mode so you can:
Set up your billing without launching a campaign
Explore the full dashboard
Learn how Google Ads really works
Can I Create an Account Without Starting a Campaign?
Yes. After switching to Expert Mode, you’ll get an option labeled:
“Create an account without a campaign”
Choosing this skips all ad setup and takes you directly to your Google Ads dashboard — ideal for those who want to set up conversion tracking, audience lists, or link Google Analytics before launching ads.
How Do I Enter My Business and Campaign Info?
Once you proceed with the Google Ads setup—either via Smart Campaign or after choosing a goal in Expert Mode—Google will guide you through entering essential business details and basic campaign configuration. This information determines who sees your ads, what they see, and where they go after clicking.
Step 1: Choose Your Advertising Goal
Google will ask, “What’s the main goal of your campaign?” Common options include:
Get more calls – Focuses on encouraging users to call your business directly.
Get more website sales or sign-ups – Optimizes for online conversions.
Get more visits to your physical location – Uses location-based targeting to drive in-store traffic.
Get more views or interactions on YouTube – For video campaigns.
Choosing the right goal helps Google optimize campaign structure, bidding, and audience targeting automatically.
Step 2: Enter Your Business Name
You’ll be prompted to input your business name, which will appear in the ad to help users recognize your brand. This is important for:
Brand recall in local or competitive markets
Displaying professionalism and legitimacy
Matching ad identity with your landing page or website
Use your official business name exactly as it appears on your website and social platforms to build trust and consistency.
Step 3: Provide Your Website URL (Optional But Recommended)
You’ll be asked to provide your website URL, which serves as the landing page users will visit after clicking your ad.
If you don’t have a website, you can still run campaigns that generate calls or visits.
If you do have a site, make sure the landing page:
Loads fast
Matches your ad message
Includes a clear call to action (CTA)
Google will preview how your website looks on mobile and desktop before proceeding.
Step 4: Review or Customize Suggested Ad Content
Based on your website and business info, Google may automatically generate a basic text ad. You can either:
Accept Google’s suggestions
Edit the ad headline, description, and display URL
Start from scratch with your own custom copy
A strong ad typically includes:
- A clear value proposition
- Relevant keywords
- A call-to-action like “Book Now,” “Shop Today,” or “Get a Quote”
How Do I Set a Budget and Target Audience?
Setting the right budget and targeting the correct audience are critical to the success of your Google Search Ads. These two factors directly affect how often your ad appears, who sees it, and how much you pay per click. Here’s how to set both correctly:
Step 1: Choose Your Daily Budget
Google Ads works on a daily budget model — you tell Google how much you’re willing to spend per day on a campaign.
For example, if your daily budget is $10, Google may spend slightly more or less on a given day, but it won’t exceed $310 in a 30-day month.
You can:
Start with a small test budget (e.g., $5–$20/day) and scale based on results.
Use tools like the Keyword Planner to estimate how much you need to spend for your target keywords.
Note: Your budget doesn’t control how much you pay per click (that’s based on your bidding strategy), but it does limit your overall exposure.
Step 2: Set Your Target Location
Google lets you precisely define where your ads appear — from country-wide to a specific pin-drop radius around a business location.
Options include:
Country-level targeting – Reach broad international or national audiences.
City or region-level targeting – Useful for regional brands or service providers.
Radius targeting (e.g., 10 km around your shop) – Ideal for local businesses.
Advanced options:
Exclude locations where you don’t want your ad to show.
Use “Presence” or “Interest” targeting to control whether ads show only to people physically in your area or also to those who’ve shown interest.
Tip: Don’t target broad areas unless you can deliver services/products there. Irrelevant impressions can waste your budget.
Step 3: Define Your Keyword Themes
In Smart Campaigns, Google asks you to enter “keyword themes.” These are topics or phrases related to your product or service — they help Google understand what searches should trigger your ads.
For example:
If you’re a plumber, keyword themes could be: “emergency plumbing,” “drain repair,” “leak detection.”
For an online shoe store: “buy running shoes,” “best sneakers online,” “affordable footwear.”
In Expert Mode, this step becomes more granular — you’ll select individual keywords and define match types:
- Broad Match
- Phrase Match
- Exact Match
Warning: Vague or overly broad themes (like “business”) may bring in unqualified clicks and waste your ad spend.
How Do I Add Billing Information?
Adding billing information is the final step before your Google Ads account becomes active and ready to serve ads. This step ensures Google can charge you appropriately based on your ad performance and budget. Here’s how it works, broken down step by step:
Step 1: Select Your Billing Country and Time Zone
When prompted, choose:
Billing country – This determines your available payment methods and tax regulations.
Time zone – Used to track your daily budget and schedule campaigns accurately.
Important: Once selected, your time zone cannot be changed later, so make sure it matches your business location or reporting preference.
Step 2: Choose a Payment Method
Google offers two primary payment methods, depending on your region:
A. Automatic Payments (Postpay)
Google charges you after your ads run — either every 30 days or when you hit a billing threshold (e.g., $500).
Best for ongoing campaigns.
B. Manual Payments (Prepay)
You load funds into your account before ads run.
Ads stop showing when your balance runs out.
Good for controlling spend or running short-term ads.
Accepted payment options include:
Credit/debit cards (Visa, Mastercard, AmEx, etc.)
Bank account (direct debit) – may require account verification.
PayPal – available in select countries.
UPI, net banking, or local wallets – available in specific regions like India, Pakistan, etc.
Not all payment methods are available in every country. Google will show only the ones available based on your selected billing country.
Step 3: Enter Business and Tax Details (if applicable)
Depending on your country, you may need to enter:
Business name and address (for invoice and tax purposes)
Tax ID or GST number (required in countries like India, Australia, and EU member states)
Providing correct tax info ensures compliance and allows you to claim tax credits where applicable.
Step 4: Accept Google Ads Terms & Conditions
Before activating the account:
Read through and accept Google Ads’ terms of service.
This outlines your rights, responsibilities, refund rules, and advertising policies.
Reminder: Violating Google Ads policies (e.g., using prohibited content) can result in account suspension — even after you’ve paid.
Step 5: Click “Submit” to Activate Your Account
Once all billing fields are filled:
Click Submit to finalize setup.
Your account becomes active.
If you created a campaign, it enters review before it starts serving ads.
You can now access your full Google Ads dashboard, monitor billing history, set spend limits, and update payment methods anytime under Tools & Settings → Billing.
What Happens After I Create the Account?
Once you’ve completed your account setup, including billing, you officially have access to the Google Ads dashboard, where all campaign activity and management happens. What you see next depends on whether you launched a campaign during setup or chose to skip it.
Scenario 1: If You Created a Campaign During Setup
Your campaign will be immediately submitted for review by Google.
The ad review process typically takes up to 24 hours, though it can be faster.
During review, your ads won’t appear in search results until approved.
Google reviews ads for:
Compliance with ad policies (e.g., no misleading claims, prohibited content)
Final URL safety and relevance
Grammar, spelling, and formatting
Tip: You can monitor the review status under Campaigns → Ads & Assets → Status column.
Scenario 2: If You Skipped Campaign Setup
If you clicked “Create an account without a campaign” (via Expert Mode), you’ll land directly on the Google Ads dashboard, but with no active campaigns. This gives you full control to:
Create search, display, video, or app campaigns from scratch
Set up conversion tracking, link Google Analytics, or import goals from GA4
Configure advanced settings like ad extensions, custom audiences, and bidding strategies
This is the preferred route for advertisers who want to build campaigns strategically instead of rushing through Smart Campaign defaults.
What Can You Do Now from the Dashboard?
Here’s what’s accessible from your Google Ads dashboard immediately after setup:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Campaigns tab | View, create, edit, or pause campaigns |
| Tools & Settings | Access billing, conversions, keyword planner, linked accounts |
| Recommendations | Google’s AI-powered suggestions to improve performance |
| Reports | Build custom performance reports |
| Billing section | View payment history, update payment methods |
Pro Tip: What Should You Do First?
After account creation (especially if you didn’t launch a campaign), your next steps should be:
Link Google Analytics (for better tracking and attribution)
Set up conversion tracking (to measure leads, sales, etc.)
Use Keyword Planner to research and finalize high-intent keywords
Organize campaigns/ad groups with a clear structure
Set realistic budgets and bidding strategies
Can I Use Google Ads Without Launching an Ad Right Away?
Yes, absolutely — you can create a fully functional Google Ads account without running or paying for a campaign immediately. This is especially useful for marketers who want to prepare everything first — tracking, audiences, billing, analytics — before investing any money.
Here’s exactly how to do it:
Step 1: Start the Sign-Up Process
Go to ads.google.com and click “Start Now.”
Sign in with your Google account.
Google will begin by pushing you into the Smart Campaign flow.
Step 2: Click “Switch to Expert Mode”
At the bottom of the Smart Campaign setup screen, you’ll see a small link labeled:
“Switch to Expert Mode”
Clicking this unlocks the full set of Google Ads features.
You’ll now have complete control over campaign types, settings, and account structure.
Many first-time users miss this button — but it’s essential for serious advertisers or those who want to explore the platform first.
Step 3: Click “Create an Account Without a Campaign”
Once you enter Expert Mode, Google will present a screen asking you to start your first campaign — but look closely at the bottom.
Click the small link: “Create an account without a campaign.”
This allows you to set up your billing profile, time zone, and currency without launching any ads.
This is ideal for agencies, businesses planning future campaigns, or learners who want to practice on the dashboard first.
Step 4: Finalize Your Basic Account Setup
You’ll be asked to:
Confirm your business info
Choose your billing country, currency, and time zone
Accept Google’s terms and conditions
Then click “Submit.”
Step 5: Access the Full Google Ads Dashboard
Once submitted, you’ll be taken to your dashboard, where you can:
Explore all features (Keyword Planner, Audience Manager, Ad Extensions, etc.)
Link tools like Google Analytics or Google Tag Manager
Configure conversion tracking before any campaign is launched
Add team members or managers to the account
Plan and draft campaigns in advance without spending a penny
Good to know: Google will not charge you until you activate and run a campaign. You can leave your account idle as long as you like.
Why This Option is Recommended for Serious Advertisers?
Creating an account without a campaign:
Gives you time to plan your ads with data and strategy
Prevents wasteful clicks due to rushed campaign setup
Allows for integration with other tools before going live
Lets you test features and reporting tools without any pressure
What is the purpose of Google Ads Search Advertising?
Google Ads Search Advertising is a platform specifically designed to help businesses and individuals create highly targeted text-based ads. The primary purpose of this platform is to:
- Capture high-intent audiences who are actively searching for products, services, or information on Google or its partner websites.
- Maximize visibility for businesses by displaying ads prominently in Google search results.
- Drive valuable actions, whether that’s website traffic, lead generation, or sales growth.
- Offer a scalable advertising solution for businesses of all sizes—be it a local shop, a startup, or a global enterprise.
The platform focuses on matching users’ search queries to relevant ads, making it one of the most precise and goal-oriented advertising options available.

For comprehensive support and detailed guidance on Google Ads, visit the Google Ads Help Center.
Who can use this platform – businesses, agencies, freelancers, or all of them?
The beauty of Google Ads Search Advertising lies in its accessibility and flexibility. It caters to a wide range of users, including:
- Businesses: From local shops to multinational corporations, any business looking to promote products or services can use Google Ads to reach its audience.
- Agencies: Digital marketing agencies often manage multiple campaigns for their clients, utilizing Google Ads’ extensive tools and analytics features.
- Marketers: Individuals responsible for growing brand visibility or product awareness can create and optimize campaigns with ease.
- Freelancers: Freelancers specializing in PPC or digital marketing can run campaigns for clients, leveraging the platform’s features to deliver measurable results.
Google Ads provides a level playing field where businesses of any size or industry can compete effectively, thanks to its scalable budgets and flexible targeting options.
Why is it considered effective for driving traffic, generating leads, and boosting sales?
Google Ads Search Advertising is highly effective for several reasons:
- Reaching High-Intent Users: It targets users who are already searching for specific products, services, or information. These users are more likely to engage with ads because they are actively looking for solutions.
- Prominent Ad Placement: Ads appear at the top and bottom of search results, ensuring they are visible to users before organic results.
- Targeted Campaigns: Advertisers can design campaigns tailored to specific keywords, demographics, locations, or even behaviors. This precision ensures businesses are connecting with the right audience.
- Measurable Results: The platform provides real-time metrics (e.g., click-through rates, conversion rates), helping advertisers understand their campaign performance and make data-driven adjustments.
- Variety of Ad Types: Options like call-only ads, dynamic search ads, and responsive search ads allow businesses to focus on specific goals such as driving phone calls or automating ad optimization.
- Scalable for Any Budget: There is no fixed minimum budget, making it accessible for small businesses while still offering enterprise-level tools for large-scale advertisers.
How Does the Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Model Work?
The Pay-Per-Click (PPC) model is an online advertising strategy where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. It’s commonly used in search engines (Google Ads, Bing Ads) and social media platforms (Facebook Ads, LinkedIn Ads).
Formula for PPC Cost


This metric shows how much revenue you earn for every dollar spent on PPC ads.

A higher CTR means your ad is relevant to users.

A higher Quality Score reduces CPC and improves ad positioning.
Example of PPC Model
- Advertiser: A Multani Blue Pottery brand runs a Google Ads campaign.
- Ad Spend: $500 is invested in Google Ads.
- CPC: The average Cost Per Click is $1.50.
- Total Clicks:
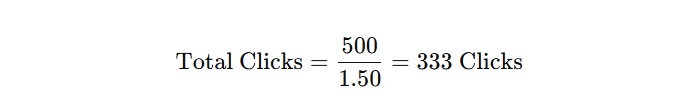
- Conversions: 10% of visitors make a purchase (33 sales).
- Revenue: Each sale is worth $50, so:
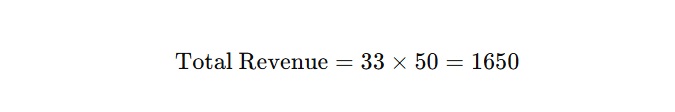
- ROAS Calculation:
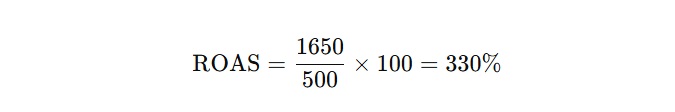
A 330% ROAS means for every $1 spent, the advertiser earns $3.30 in return.
What does cost-per-click (CPC) Mean?
Cost-Per-Click (CPC) is a metric used in online advertising that represents the amount an advertiser pays each time a user clicks on their ad. It’s a fundamental component of pay-per-click (PPC) advertising models, commonly utilized in platforms like Google Ads and social media networks.
Formula to Calculate CPC:

Example:
Suppose an advertiser spends $200 on a PPC campaign, and the ad receives 400 clicks. The CPC would be calculated as follows:

This means the advertiser pays $0.50 for each click on their ad.
Understanding CPC is crucial for advertisers to manage their budgets effectively and assess the cost-effectiveness of their advertising campaigns. A lower CPC indicates a more cost-efficient campaign, allowing advertisers to achieve more clicks within their budget.
What does cost-per-impression (CPM) mean?
Cost-Per-Impression (CPI), also known as Cost-Per-Mille (CPM), is a metric used in advertising to denote the cost an advertiser pays for one thousand impressions of their ad. An “impression” occurs each time an ad is displayed to a user, regardless of whether it’s clicked. This model is prevalent in various media, including online platforms, television, radio, and print.
Formula to Calculate CPM:

Example:
Suppose an advertiser spends $500 on a campaign that generates 200,000 impressions. The CPM would be calculated as follows:

This means the advertiser pays $2.50 for every 1,000 times their ad is displayed.
Understanding CPM is crucial for advertisers to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of their campaigns and to compare expenses across different advertising channels. A lower CPM indicates a more cost-efficient campaign, allowing advertisers to reach a larger audience within their budget.
Ad Auctions and Ad Rank:
Every time someone performs a search, Google runs an ad auction to determine which ads are shown and in what order.
Ad Rank (calculated based on the advertiser’s bid, ad quality, and expected impact) ensures that users see the most relevant and useful ads.
Efficiency and Control:
Advertisers have full control over their budgets and can set daily limits to avoid overspending.
PPC ensures that businesses get measurable value for their investment by targeting only engaged users.
Google Ads Search Advertising is a highly efficient and customizable platform designed to connect advertisers with audiences who are already searching for what they offer. By leveraging the PPC model, businesses ensure cost-efficiency and maximize their return on investment. Whether you’re a freelancer or a global enterprise, this platform provides the tools to drive results at any scale.
Learn more about how Google Ads auctions and bidding work by visiting the official Google Ads Auction and Bidding Guide.
Where do Google Ads get displayed on search result pages?
Google Ads appear in two key positions on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP):
- Top of the Page: Ads displayed here are highly visible and are the first thing users see when they perform a search. This placement ensures maximum attention and typically generates the most clicks because users tend to engage with results at the top.
- Bottom of the Page: Ads placed here also benefit from visibility, especially for users who scroll down after viewing organic results. These placements often serve as a second chance to capture user interest.
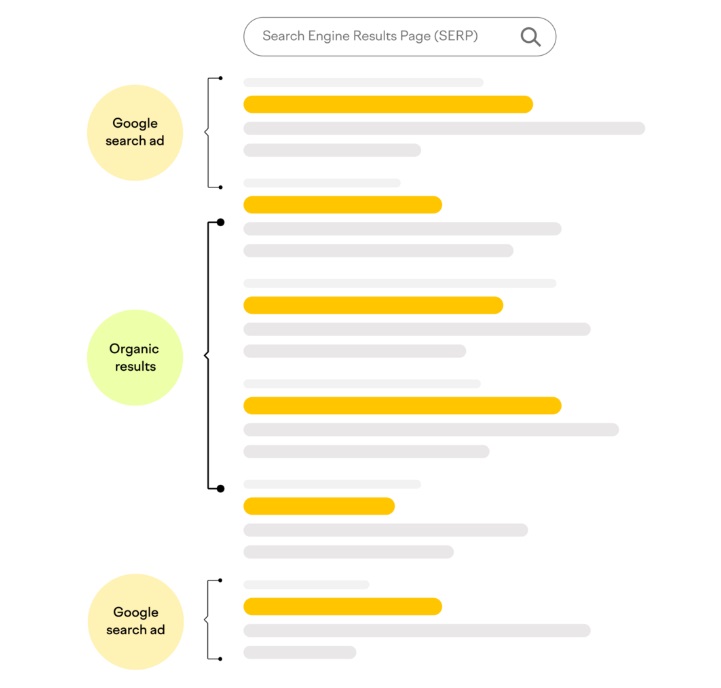
Both positions are strategically chosen to make ads prominent and allow advertisers to engage with users actively searching for solutions.
How do ad placements at the top and bottom of search results improve visibility?
Ad placements in these positions improve visibility in the following ways:
- Top Placements: Ads at the top stand out because they appear before any organic search results, making them more likely to be clicked. This ensures advertisers can reach users before they even consider scrolling down to organic listings.
- Bottom Placements: While not as prominent as top placements, ads at the bottom catch the attention of users who carefully review results. These ads provide an opportunity to engage users who may have skipped over the initial top ads or organic results.
The combination of top and bottom placements ensures ads are visible to different types of searchers, maximizing the chances of engagement.
What are the main campaign types available for search ads?
Google Ads offers several campaign types tailored to meet specific advertising goals. Here’s a closer look:
1. Standard Search Ads
- What They Are: Standard search ads are the most common type of text-based ads. They appear when users search for specific keywords relevant to the advertiser’s offerings.
- When to Use Them: Ideal for businesses aiming to capture high-intent users who are actively searching for their products or services.
- Key Benefits:
- Straightforward and easy to set up.
- Allows advertisers to craft precise ad copy targeting specific search intents.
- Highly effective for driving website traffic or lead generation.
2. Dynamic Search Ads
- How They Work: Dynamic search ads automatically generate ad headlines and landing pages based on the content of the advertiser’s website. These ads dynamically match user search queries with relevant website pages.
- When to Use Them:
- Suitable for businesses with large websites or extensive product catalogs, where manually creating ads for each page or keyword would be time-consuming.
- Effective for capturing traffic from less obvious or long-tail search queries.
- Key Benefits:
- Saves time as there’s no need to create individual ads for every product or service.
- Increases reach by targeting broader or unexpected search queries.
- Ensures users are directed to the most relevant landing page.
3. Responsive Search Ads
- What Makes Them Unique: Responsive search ads use AI-driven optimization to test multiple combinations of headlines and descriptions. Google’s algorithm automatically determines the best-performing combinations to show to users.
- When to Use Them: Perfect for advertisers looking to maximize performance through automated testing and optimization.
- Key Benefits:
- Greater flexibility: Advertisers can input up to 15 headlines and 4 descriptions.
- Improved performance: AI optimizes the ad based on user behavior and preferences.
- Personalized experience: Ads dynamically adjust to match user intent, increasing engagement.
4. Call-Only Ads
- How They Work: Call-only ads are specifically designed to drive phone calls. These ads focus on users who are more likely to pick up the phone rather than visit a website.
- When to Use Them: Ideal for service-based businesses or industries where phone calls are a key driver of leads or conversions, such as healthcare, legal services, or home repairs.
- Key Benefits:
- Encourages immediate contact: Users can directly call the business without needing to visit a website.
- Mobile-focused: Perfect for capturing traffic from users searching on mobile devices.
- Highly targeted: Effective for local businesses looking to connect with nearby customers quickly.

Each campaign type offers unique features and benefits, allowing advertisers to tailor their approach based on their goals. Whether it’s targeting specific keywords with standard ads, automating with dynamic ads, optimizing performance with responsive ads, or driving calls with call-only ads, Google Ads ensures businesses can connect with their target audience in the most effective way possible.
Manage your ad preferences and control the types of ads you see with Google Ad Center.
What Other Campaign Options Can Be Explored?
Google Ads extends beyond search ads, offering several specialized campaign options that cater to broader advertising goals. These campaigns are designed to reach audiences across multiple platforms, deliver specific outcomes, and drive engagement.
1. Performance Max Campaigns
What Are They? Performance Max Campaigns are a goal-based, fully automated campaign type that enables advertisers to expand their reach across Google’s entire ecosystem, including:
- YouTube
- Gmail
- Google Discover
- Google Maps
- Display Network
These campaigns use machine learning to optimize performance and help achieve specific goals like sales, leads, or website traffic.
How Do They Work?
Advertisers input creative assets (headlines, descriptions, images, and videos), goals, and target audiences.
Google’s AI combines these assets into different ad formats and determines the best-performing combinations.
It automatically decides where and when to show ads across the Google network to maximize results.
When Should You Use Them?
Ideal for businesses that want to simplify their advertising efforts and leverage Google’s AI to automate performance optimization.
Suitable for advertisers aiming for multi-channel campaigns to reach users across platforms seamlessly.
Key Benefits:
- Broader Reach: Ads appear on diverse platforms, maximizing exposure.
- Automation: AI manages bidding, placements, and creative optimization, reducing manual effort.
- Goal-Oriented: Campaigns are optimized to achieve specific targets like increasing conversions or driving in-store visits.
2. Shopping Ads
What Are They? Shopping Ads are product-focused ads that display a product’s image, price, title, and store name directly within Google Search results. They also appear on the Google Shopping tab.
How Do They Work?
Advertisers upload a product feed containing details like product names, images, prices, and availability through Google Merchant Center.
When users search for products, Google matches their queries with relevant items from the product feed.
Ads are displayed with images and pricing, providing users with quick and visual information about the products.
When Should You Use Them?
Designed for e-commerce businesses looking to drive online sales.
Effective for showcasing physical products and capturing high-intent shoppers actively searching for items.
Key Benefits:
- Visual Appeal: Product images make the ads stand out compared to regular text ads.
- Increased Relevance: Ads display specific product details, ensuring users see exactly what they’re looking for.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Users who click on Shopping Ads are typically closer to making a purchase decision.
3. Local Ads
What Are They? Local Ads are designed to help brick-and-mortar businesses attract customers by targeting users searching for nearby services or locations. These ads are focused on driving in-store visits, calls, or local interactions.
How Do They Work?
Advertisers input their business location and create ads that highlight store-specific information (e.g., address, hours of operation).
Google uses location targeting and search intent to display ads to users nearby or actively looking for local businesses.
Ads can appear on Google Search, Maps, and other partner platforms, ensuring maximum reach for local audiences.
When Should You Use Them?
Perfect for local businesses such as restaurants, cafes, retail stores, or service providers like salons and repair shops.
Effective for driving foot traffic or local engagement, especially for businesses in competitive regional markets.
Key Benefits:
- Hyperlocal Targeting: Ads reach users within specific geographical areas or zip codes.
- Action-Oriented: Designed to prompt users to call, visit, or get directions to the business.
- Visibility on Google Maps: Local Ads ensure businesses are prominently displayed when users search for nearby options.
Each of these campaign options provides businesses with powerful tools to achieve their advertising objectives:
- Performance Max Campaigns: Deliver multi-channel reach and automated optimization for businesses targeting diverse platforms.
- Shopping Ads: Focus on e-commerce growth by showcasing product visuals and pricing to high-intent shoppers.
- Local Ads: Empower local businesses to connect with nearby customers and increase foot traffic or direct interactions.
These campaigns are tailored to suit different advertising goals, helping businesses effectively engage with their target audience in the most impactful ways possible.
How Does Targeting Work in Google Ads?
Targeting in Google Ads is one of its most powerful features, enabling advertisers to connect with highly specific audiences. Advertisers can ensure their ads reach the right users at the right time, by using a combination of keywords, audiences, and demographics. Let’s dive into each targeting option:
Keyword Targeting: What are the different types, and how do they work?
Keyword targeting is the cornerstone of search advertising. It allows advertisers to show ads to users based on specific search terms. Keywords can be targeted using three primary match types:
Broad Match:
Broad match casts the widest net. Ads appear when a user searches for variations of the keyword, including synonyms, related searches, and even misspellings.
Example: For the keyword “running shoes,” the ad might show for searches like “buy sneakers,” “jogging footwear,” or “best shoes for running.”
Ideal for generating a large volume of traffic and discovering new keyword opportunities.
Phrase Match:
Ads are shown when the user’s query includes the exact phrase or a close variation, with words either before or after the phrase.
Example: For the keyword “running shoes,” ads might appear for “best running shoes for men” or “running shoes sale.”
Best for targeting specific intents while still allowing some flexibility in search queries.
Exact Match:
Ads are triggered only when the user’s search matches the keyword exactly or includes close variations (e.g., singular/plural forms).
Example: For the keyword “running shoes,” the ad will only show for searches like “running shoes” or “buy running shoes.”
Perfect for highly targeted campaigns where precision is key.

Why it’s important!
- Combining these match types allows advertisers to balance reach and precision.
- Keyword targeting ensures ads are shown only to users whose search queries align with the business’s offerings.
Audience Targeting: How do in-market and affinity audiences help target users?
Google Ads allows advertisers to go beyond keywords by targeting users based on their behavior, interests, and intentions through two main audience types:
In-Market Audiences:
These are users actively researching or comparing products and services. Google identifies these users based on recent browsing and search behaviors.
Example: A user looking up “best smartphones under $500” or comparing phone reviews would fall into the “Mobile Phones” in-market audience.
Ideal for businesses targeting users who are ready to make a purchase or take action soon.
Affinity Audiences:
These are users with long-term interests or hobbies that align with certain products or industries.
Example: Someone who frequently visits tech blogs or watches tech reviews might fall into the “Tech Enthusiasts” affinity audience.
Great for building brand awareness and targeting users who may not be immediately ready to buy but have a strong interest in the category.
Customer Match: What is it, and how does it work for retargeting?
Customer Match enables advertisers to target users from their own customer data. Here’s how it works:
Advertisers upload a contact list (e.g., email addresses, phone numbers) to Google Ads.
Google matches the data with users logged into their Google accounts.
Ads are then shown to these users across Google platforms like Search, YouTube, and Gmail.
Use Cases:
- Retargeting existing customers to encourage repeat purchases or loyalty.
- Cross-selling or upselling to current customers.
- Re-engaging inactive customers with personalized offers.
Why it’s effective!
Targets users who already have a relationship with the brand. Drives higher ROI since these users are more likely to convert.
Geographical Targeting: How does it focus on specific areas?
Geographical targeting allows advertisers to define the locations where their ads will appear. This can range from hyperlocal to global:
Hyperlocal Targeting:
Advertisers can target specific zip codes, neighborhoods, or even a small radius around their business.
Example: A coffee shop targeting users within a 2-mile radius to promote morning discounts.
Regional or National Targeting:
Businesses can target users across cities, states, or entire countries.
Example: A national retailer running a campaign for an upcoming holiday sale.
Global Targeting:
Companies with an international presence can target users worldwide or exclude specific regions if needed.
Key Benefits:
- Tailored campaigns ensure ads are only shown to users in relevant areas, reducing wasted spend.
- Geographical targeting is crucial for local businesses and businesses offering region-specific services.
Lookalike Audiences: How do they help find similar customers?
Lookalike audiences (also known as Similar Audiences in Google Ads) allow advertisers to target users who share characteristics with their existing customers. Here’s how they work:
How they’re created:
Google analyzes the data from an advertiser’s Customer Match list or website visitors.
It identifies patterns and creates a new audience segment of users with similar behaviors or interests.
Why are they effective?
They expand reach to users who are more likely to engage or convert based on their similarity to current customers.
Advertisers can effectively find new leads without guessing which demographics to target.
Example:
If an advertiser uploads a list of loyal customers who frequently purchase high-end products, Google can create a lookalike audience of users with similar spending habits or interests.
Demographic Targeting: Can advertisers segment users based on demographics?
Yes, Google Ads allows advertisers to segment their audience using a range of demographic factors, including:
- Age: Target users within specific age groups (e.g., 18-24, 25-34).
- Gender: Focus on male, female, or all users.
- Income Levels: Reach users in specific income brackets (e.g., top 10%, middle 50%).
- Parental or Marital Status: Advertisers can target parents or non-parents and even people based on their marital status.
Why it matters:
- Demographic targeting ensures ads resonate with specific groups of people, improving relevance and performance.
- It’s particularly useful for products or services with niche appeal (e.g., wedding planning services targeting engaged couples or luxury items aimed at high-income individuals).
Google Ads provides advertisers with a comprehensive suite of targeting options to connect with the most relevant audiences:
- Keyword Targeting: Match ads to users’ search queries using broad, phrase, or exact match.
- Audience Targeting: Focus on in-market and affinity audiences to target users based on intent or long-term interests.
- Customer Match: Retarget existing customers using uploaded contact lists.
- Geographical Targeting: Narrow down ads by location, from local zip codes to global markets.
- Lookalike Audiences: Discover new customers with characteristics similar to existing ones.
- Demographic Targeting: Segment users by age, gender, income, or marital status.
These options allow advertisers to create highly personalized and efficient campaigns, ensuring ads reach the right people, at the right time, and in the right place.
How Can Ads Be Made More Engaging?
Creating engaging ads is crucial for capturing the attention of users and encouraging them to interact. Google Ads provides several tools and features that allow advertisers to customize and enhance their ads, making them more appealing and effective.
Well explained by “Edvinas”
Customizing Ad Copy and Display URLs
Ad Copy Customization
Ad copy is the first thing users see when your ad appears in search results. Crafting compelling, relevant, and action-oriented ad copy significantly improves user engagement.
What can be customized?:
Headlines: Create attention-grabbing headlines that directly address user intent or highlight a unique selling proposition (USP).
Descriptions: Include concise but impactful descriptions that emphasize benefits, offers, or solutions to the user’s problem.
Call-to-Actions (CTAs): Use action-oriented phrases like “Shop Now,” “Get a Free Quote,” or “Book Today” to drive clicks.
Customizing Display URLs
What are display URLs?: These are the URLs shown in the ad, which may differ from the actual landing page URL.
How they work!
Advertisers can edit the display URL to include keywords or make it more relevant to the user’s search query.
Example: Instead of displaying the actual URL www.example.com/product12345, you could show www.example.com/Running-Shoes to align with the ad copy.
Benefits of Customization:
- Improved Relevance: Customizing ad copy and display URLs ensures the ad closely matches user search intent.
- Higher Engagement: Clear and relevant messaging encourages more clicks.
- Increased Trust: Display URLs that reflect the product or service reassure users about the ad’s credibility.
Making Ads More Interactive with Extensions
Ad extensions enhance the visibility and functionality of ads, providing users with more information or actions they can take. Here are the key types of extensions and their benefits:
Sitelink Extensions
Sitelink extensions add additional links below the main ad, directing users to specific pages on your website.
Example: For a clothing store, sitelinks could include “New Arrivals,” “Men’s Clothing,” “Women’s Clothing,” or “Clearance Sale.”
Benefits:
- Improved Navigation: Users can quickly find the exact page they’re looking for, reducing friction.
- More Click Opportunities: Multiple links increase the chances of user interaction.
- Boosted CTR: Ads with sitelink extensions are more visually prominent and engaging.
Callout Extensions
Callout extensions are short snippets of text that highlight key features or offers, such as “Free Shipping,” “24/7 Support,” or “Satisfaction Guaranteed.”
Benefits:
- Showcase USPs: Callouts help communicate unique selling points effectively.
- Add Value: They provide additional context or incentives for users to click.
- Enhance Visibility: Callouts make ads stand out by including more information.
Image Extensions
Image extensions add a visual element to the ad, such as a product image, brand logo, or promotional banner.
Benefits:
- Visual Appeal: Ads with images are more attention-grabbing.
- Increased Engagement: Visuals often communicate more effectively than text alone.
- Brand Recognition: Including a logo or branded image reinforces brand identity.
Other Common Extensions
- Call Extensions: Include a phone number so users can call directly from the ad.
- Location Extensions: Display a business’s address or map link to encourage in-store visits.
- Price Extensions: Showcase prices for specific products or services.
Adding Valuable Details with Structured Snippets
What Are Structured Snippets?
Structured snippets are predefined headers with lists of specific information about your products or services. Examples of headers include:
- Types: “Types of Services,” “Product Categories,” or “Available Models.”
- Features: “Amenities,” “Destinations,” or “Styles.”
How Do They Work?
- Advertisers select a relevant header (e.g., “Brands”) and provide a list of details under it (e.g., “Nike, Adidas, Puma”).
- These snippets appear below the ad description, providing additional context about what the business offers.
Benefits of Structured Snippets:
- Highlight Key Details: They quickly communicate important aspects of your offerings, helping users make informed decisions.
- Improve Relevance: By providing specific details, structured snippets make the ad more aligned with user intent.
- Enhance Credibility: Adding detailed information builds trust with users, as it shows transparency about the business or product.
So,
- Customizing Ad Copy and Display URLs:
- Craft relevant headlines and descriptions that align with user intent.
- Use display URLs to reinforce credibility and improve ad relevance.
- Leveraging Ad Extensions:
- Use sitelinks to direct users to specific landing pages.
- Highlight key features or offers with callout extensions.
- Add visual appeal with image extensions.
- Using Structured Snippets:
- Provide additional details about products or services using predefined headers.
Advertisers can create ads that are not only visually appealing but also more relevant, interactive, and informative, leading to better user engagement and higher conversion rates.
How Does Google Use AI for Campaign Optimization?
Google Ads leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to simplify campaign management, improve performance, and achieve specific advertising goals. Through advanced AI-powered bidding strategies and optimization tools, advertisers can save time while maximizing results.
What Are AI-Powered Bidding Strategies, and How Do They Help Advertisers?
AI-powered bidding strategies use machine learning to optimize bids in real-time, ensuring advertisers get the most out of their budget. These strategies are tailored to achieve specific objectives, whether it’s driving conversions, increasing revenue, or maximizing clicks.
Let’s explore the main bidding strategies:
Target CPA (Cost-Per-Acquisition) Bidding
This strategy focuses on acquiring leads or conversions at a specific cost. Google’s AI automatically adjusts bids to help achieve the desired cost-per-conversion (CPA).
- Advertisers set a target CPA (e.g., $20 per lead).
- Google analyzes historical data and user behavior to bid higher on searches likely to convert within the target CPA.
- Lower bids are placed on searches less likely to convert, ensuring cost-efficiency.
Best For:
Businesses looking to maximize conversions while staying within a specific budget. Campaigns with sufficient historical conversion data to help AI optimize performance.
Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) Bidding
Target ROAS aims to maximize revenue based on the return advertisers want for every dollar spent.
- Advertisers set a target ROAS (e.g., 400%).
- Google uses machine learning to predict the revenue potential of each auction and adjusts bids accordingly.
- High bids are placed on clicks likely to generate high returns, while lower bids are applied to less promising opportunities.
Best For:
E-commerce or retail campaigns where sales revenue is directly tied to ad performance. Advertisers with a clear understanding of their desired profitability.
Maximize Conversions Bidding
This strategy aims to drive as many conversions as possible within a campaign’s budget.
Google’s AI automatically bids higher for users and keywords more likely to convert.
The focus is on volume rather than controlling the cost-per-conversion.
Best For:
- Advertisers with flexible budgets looking to prioritize conversion volume over cost control.
- New campaigns that don’t yet have a defined CPA target.
Explained “How AI is changing Google Ads” by Aaron Young
What Tools Does Google Offer for Campaign Refinement?
In addition to AI-driven bidding strategies, Google provides a suite of tools to help advertisers refine their campaigns and improve performance. These tools ensure advertisers make informed decisions based on data and insights.
Keyword Planner
A research tool that helps advertisers identify the best keywords to target.
Advertisers enter seed keywords or topics. The tool suggests related keywords, along with metrics like search volume, competition, and estimated CPC (Cost-Per-Click).
It also provides seasonal trends, helping advertisers align campaigns with user demand.
Benefits:
- Helps discover high-performing keywords that align with business goals.
- Ensures campaigns are optimized for relevant search queries.
- Reduces wasted spend by targeting keywords with the highest potential ROI.
Auction Insights
A competitive analysis tool that provides data on how an advertiser’s performance compares to competitors in the same ad auctions.
Shows metrics like Impression Share (percentage of impressions an ad received out of total possible impressions), Overlap Rate (how often a competitor’s ad appeared alongside yours), and Position Above Rate (how often a competitor’s ad ranked higher than yours).
Offers visibility into competitor performance without revealing sensitive data.
Benefits:
- Helps advertisers understand their position in the market.
- Identifies opportunities to improve ad rank or impression share.
- Allows strategic adjustments to bidding, targeting, or budget allocation.
Conversion Tracking
A tracking tool that measures specific user actions (e.g., purchases, form submissions, calls) after interacting with an ad.
Advertisers place a conversion tag (snippet of code) on their website, app, or landing page.
When a user completes the desired action, the tag records the conversion and links it back to the ad campaign.
Google provides detailed reports on conversions, including metrics like cost-per-conversion, conversion rate, and total conversions.
Benefits:
- Accurately measures campaign performance and ROI.
- Identifies which ads, keywords, or audiences drive the most conversions.
- Enables data-driven optimization to improve future campaigns.
Key Benefits of AI-Powered Optimization
By combining AI-powered bidding strategies with tools like Keyword Planner, Auction Insights, and Conversion Tracking, advertisers gain several advantages:
Automation Saves Time:
AI takes care of bid adjustments and optimization, freeing advertisers to focus on strategy and creativity.
Improved Efficiency:
Bids and budgets are optimized for maximum results, minimizing wasted spend.
Real-Time Adjustments:
AI continuously analyzes user behavior and campaign performance, making instant adjustments for better outcomes.
Data-Driven Decisions:
Tools like Auction Insights and Conversion Tracking provide actionable insights to refine campaigns and outpace competitors.
Google Ads’ AI-powered bidding strategies (Target CPA, Target ROAS, Maximize Conversions) and refinement tools (Keyword Planner, Auction Insights, Conversion Tracking) work together to optimize campaigns effectively. These features ensure advertisers not only save time but also achieve specific goals like maximizing conversions, improving ROI, or driving revenue. With these advanced tools, Google Ads empowers businesses to stay competitive and make the most of their advertising budgets.
How Can Insights Be Enhanced Through Integrations?
Google Ads becomes significantly more powerful when integrated with tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4), Google Tag Manager, and third-party CRMs such as HubSpot or Salesforce. These integrations provide deeper insights, streamline workflows, and enable more informed decision-making for advertisers.
How Does Integrating Google Ads with Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Improve Performance Tracking?
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is Google’s advanced analytics platform designed to provide a holistic view of user interactions across websites, apps, and ads. Integrating Google Ads with GA4 creates a seamless flow of data between the two platforms, unlocking valuable insights. Here’s how it works:
What does Integration Do?
Import Campaign Data into GA4: Advertisers can view detailed Google Ads performance data, such as impressions, clicks, and costs, directly in GA4.
Track User Behavior Beyond Clicks: GA4 tracks how users interact with a website or app after clicking on an ad, providing insights into their journey.
Measure Conversions Across Devices: GA4’s cross-device tracking enables advertisers to see how users engage across multiple devices and touchpoints.
Key Benefits
Deeper Understanding of Customer Behavior:
Learn what happens after a user clicks on an ad: Do they explore multiple pages, abandon the cart, or complete a purchase?
Identify high-performing landing pages or areas where users drop off, allowing for website or campaign optimization.
Improved Conversion Tracking:
Measure important actions like form submissions, video views, or purchases and attribute them to specific campaigns or keywords in Google Ads.
GA4 provides event-based tracking, which is more flexible than the older Universal Analytics system.
Audience Insights for Retargeting:
GA4 allows advertisers to create detailed audience segments based on user behavior, such as people who abandoned their carts or spent a specific amount of time on the site.
These audience segments can then be synced with Google Ads for retargeting campaigns.
Attribution Insights:
GA4 includes advanced attribution models (e.g., data-driven attribution) that show the role each touchpoint—like a Google Ads click or organic search—plays in driving conversions.
This helps advertisers optimize their budgets by investing in the most effective channels.
Use Case Example:
A retailer running Google Ads can use GA4 to analyze which keywords drive not only clicks but also purchases. If a specific keyword generates many clicks but no conversions, they can adjust their bidding strategy or optimize their landing page.
What is the Role of Google Tag Manager in Streamlining Workflows?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a tool that simplifies the process of adding and managing tracking codes (tags) on a website or app. When integrated with Google Ads, it provides a streamlined way to set up conversion tracking and monitor user interactions without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
What GTM Does?
Allows advertisers to add, update, and manage tags (like Google Ads conversion tags) without directly editing website code.
Supports a wide range of tags, including Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, and custom tracking scripts.
Key Benefits
Simplified Conversion Tracking:
Advertisers can set up conversion events, such as purchases, form submissions, or button clicks, directly in GTM.
Eliminates the need for developers to add tracking codes manually.
Error Reduction:
GTM’s debugging and preview tools allow advertisers to test tags before they go live, ensuring they work correctly.
Reduces the risk of misconfigured or missing tags, which could lead to inaccurate data.
Flexibility for Marketers:
Marketers can make changes to tracking setups independently, saving time and avoiding bottlenecks caused by waiting for developer support.
Seamless Integration with Google Ads:
Automatically sends conversion data to Google Ads, enabling accurate measurement of ad performance and ROI.
Ensures that remarketing tags are properly implemented, making it easier to retarget users who interacted with the website.
Use Case Example:
A travel agency can use GTM to track when users click on a “Book Now” button. This data is sent to Google Ads to measure how effective specific campaigns are at driving bookings.
Learn more about managing and monetizing your ad inventory with Google Ad Manager.
What Is the Role of Third-Party CRMs (Like HubSpot or Salesforce)?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools like HubSpot or Salesforce help businesses manage and analyze customer data. When integrated with Google Ads, these tools enable a two-way data sync that enhances lead management and campaign performance.
How the Integration Works?
Businesses can upload customer lists (e.g., email addresses, phone numbers) from their CRM to create Customer Match campaigns.
Google Ads matches this data with users logged into Google accounts, enabling targeted advertising.
Export Lead Data from Google Ads to CRMs:
Leads generated through Google Ads (e.g., form submissions from a lead-gen ad) can be automatically sent to the CRM.
This allows sales teams to follow up on leads quickly and effectively.
Key Benefits
Enhanced Retargeting:
Use CRM data to create highly targeted campaigns. For example, target existing customers with upsell or cross-sell offers.
Exclude existing customers from acquisition campaigns to focus on new prospects.
Better Lead Tracking and Nurturing:
CRMs can track leads from the moment they interact with an ad to when they make a purchase or sign a contract.
Enables personalized follow-ups based on where the lead is in the sales funnel.
Closed-Loop Reporting:
Integrating Google Ads with CRMs provides a clear picture of which ads generate high-quality leads or revenue.
Advertisers can connect ad spend to actual business outcomes (e.g., how much revenue was driven by a specific campaign).
Streamlined Workflows:
Automating the flow of data between Google Ads and CRMs reduces manual work and ensures timely follow-ups.
Sales and marketing teams can collaborate more effectively, using shared data to refine campaigns and close more deals.
Use Case Example:
A B2B software company integrates Salesforce with Google Ads. Leads captured through Google Ads are automatically sent to Salesforce, where the sales team can see which campaign generated the lead and track their progress through the sales pipeline.
Integrating Google Ads with tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4), Google Tag Manager, and third-party CRMs like HubSpot or Salesforce enhances the depth and accuracy of insights. Here’s why it matters:
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4): Provides advanced tracking of user behavior and conversion data, enabling better campaign optimization and audience targeting.
- Google Tag Manager: Simplifies tag management, ensures accurate tracking, and reduces dependency on developers.
- Third-Party CRMs: Facilitates seamless lead management, improves retargeting, and connects ad performance to actual business outcomes.
These integrations empower advertisers to make data-driven decisions, streamline their workflows, and maximize the effectiveness of their Google Ads campaigns.
What Performance Metrics Should Advertisers Track?
Performance metrics in Google Ads are crucial for measuring the effectiveness of campaigns and making data-driven optimizations. These metrics help advertisers understand how their ads are performing, whether they are achieving their goals, and where improvements are needed.
What Does Click-Through Rate (CTR) Indicate About Ad Engagement?
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a percentage that shows how often people who see your ad click on it.
It is calculated using the formula:
CTR = (Clicks / Impressions) × 100
Why is CTR Important?
Measures Ad Relevance:
A high CTR indicates that your ad is relevant to the audience and resonates with their search intent.
A low CTR may suggest that the ad copy, keywords, or targeting needs improvement.
Affects Quality Score:
CTR is a key component of Google’s Quality Score (a metric that determines ad rank and cost-per-click). Higher CTRs improve Quality Score, leading to:
- Lower CPC (Cost-Per-Click).
- Better ad placement.
Indicates Engagement:
CTR reflects how effectively your ad captures attention and compels users to take action.
How to Improve CTR?
- Use compelling headlines that directly address user intent.
- Include strong Call-to-Actions (CTAs) like “Shop Now” or “Learn More.”
- Leverage ad extensions (e.g., sitelinks, callouts) to provide additional context and clickable options.
Industry Benchmarks:
CTR benchmarks vary by industry, but an average CTR for search ads is around 3-5%. Higher CTRs are common in highly targeted campaigns.
How is Conversion Rate Used to Measure Ad Success?
Conversion Rate measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action after clicking on your ad.
Conversion Rate = (Conversions / Clicks) × 100
Why is Conversion Rate Important?
It shows how effective your ad and landing page are at driving actions like purchases, sign-ups, or downloads.
Helps Identify Bottlenecks:
A low conversion rate may indicate issues such as:
- Poor landing page experience.
- Mismatch between ad copy and the landing page content.
- Targeting the wrong audience.
Optimizes ROI:
A higher conversion rate means more value from your ad spend, resulting in better returns.
How to Improve Conversion Rate?
Ensure the landing page aligns with the ad copy and provides a seamless user experience.
Simplify the conversion process (e.g., fewer form fields or clear CTAs). Use A/B testing to experiment with different ad creatives, CTAs, and landing pages.
Leverage audience targeting to reach users more likely to convert.
Industry Benchmarks:
Average conversion rates vary widely by industry but typically range from 2-5%. Some industries, like finance or e-commerce, may see higher rates due to high-intent audiences.
Why is Tracking Cost-Per-Conversion Important for ROI?
Cost-Per-Conversion (also called Cost-Per-Acquisition or CPA) is the average amount an advertiser spends to generate a conversion.
Cost-Per-Conversion = Total Ad Spend / Total Conversions
Measures Campaign Efficiency:
CPA shows how efficiently your campaign is turning ad spend into valuable outcomes.
A low CPA means you’re acquiring leads, sales, or actions at a lower cost, maximizing ROI.
Helps Set Budgets:
Tracking CPA helps advertisers determine whether their campaigns are profitable and where they can scale spending.
Evaluates Bid Strategies:
Advertisers can use CPA to assess the performance of Target CPA Bidding or other automated bidding strategies.
How to Optimize Cost-Per-Conversion?
Target High-Intent Keywords: Focus on keywords that attract users more likely to convert.
Improve Ad Relevance: Ensure your ad copy directly addresses the audience’s needs.
Enhance Landing Pages: Optimize your landing pages for speed, usability, and relevance to the ad.
Use Smart Bidding: Leverage Google’s Target CPA bidding to automate bid adjustments for conversions.
Industry Benchmarks:
CPA benchmarks vary by industry and campaign goals. For example:
- E-commerce campaigns may aim for a CPA as low as $10-$50 per sale.
- B2B campaigns targeting high-value leads may have higher CPAs, such as $100-$200.
Stay updated with the latest tutorials, insights, and best practices by subscribing to the official Google Ads YouTube Channel.
How Can Advertisers Monitor and Improve Their Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)?
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
ROAS = Revenue / Ad Spend
Why is ROAS Important?
Measures Profitability:
- ROAS shows whether your campaigns are generating enough revenue to justify their costs.
- A ROAS of 4:1 means you earn $4 in revenue for every $1 spent on ads.
Drives Strategic Decisions:
High-performing campaigns with strong ROAS can be scaled up, while underperforming campaigns may need adjustments or discontinuation.
Industry-Specific Insights:
ROAS goals vary based on profit margins and business models. For example:
- Retailers with low-profit margins may require a ROAS of 6:1 or higher.
- Subscription services with recurring revenue may succeed with a ROAS of 2:1.
How to Improve ROAS?
Focus on High-Value Products: Promote products or services with higher profit margins.
Refine Audience Targeting: Use customer match, lookalike audiences, or in-market audiences to target users likely to make larger purchases.
Optimize Campaign Budgets: Allocate more budget to campaigns with proven ROAS and scale back underperforming ones.
Leverage Smart Bidding: Use Google’s Target ROAS Bidding to automatically optimize bids for revenue generation.
Tracking ROAS:
ROAS can be monitored in Google Ads’ reporting dashboard or through integrations with tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) or CRMs (e.g., Salesforce).
Tracking and optimizing these four metrics is essential for the success of Google Ads campaigns:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR) measures how effectively ads capture user attention.
- Conversion Rate evaluates the success of ads in driving desired user actions.
- Cost-Per-Conversion assesses the efficiency of turning ad spend into valuable results.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) determines the profitability of campaigns.
advertisers can improve performance, reduce wasted spend, and maximize the overall impact of their Google Ads campaigns, by consistently monitoring these metrics and making data-driven adjustments.
How Do E-Commerce Brands Use Shopping Ads to Boost Online Sales?
Shopping Ads are visually rich, product-focused advertisements that showcase an image, title, price, and store name directly within Google Search results and the Shopping tab.
Why Are They Ideal for E-Commerce?
Product Showcase: E-commerce brands can highlight their products visually, which attracts more attention compared to plain text ads.
High Purchase Intent: Shopping Ads target users actively searching for specific products, making them more likely to convert.
Automated Targeting: These ads automatically pull product information from a business’s Google Merchant Center feed, ensuring relevance to user queries.
Key Benefits for E-Commerce Brands
- Increased Visibility: Products appear at the top of search results, often above traditional search ads.
- Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR): The combination of images and pricing makes these ads more engaging.
- Ease of Comparison: Users can compare products from different stores directly within the ad format, simplifying their purchase decision.
Example Use Case
An online shoe retailer uses Shopping Ads to promote its best-selling sneakers. When users search for “buy running shoes,” the retailer’s ad shows the product image, price, and brand name. This visibility leads to more clicks and purchases.
Well Explained by “Aaron Young“
Why Are Local Businesses Ideal Candidates for Local Ads?
Local Ads are designed to help brick-and-mortar businesses attract nearby customers. These ads focus on driving in-store visits, calls, or directions.
Why Are They Effective for Local Businesses?
Hyperlocal Targeting: Local Ads use geographical targeting to reach users within a specific area or radius.
Location Prominence: Ads appear on Google Search, Google Maps, and other platforms, ensuring visibility when users search for nearby services or products.
Immediate Actions: Features like “Call Now” or “Get Directions” encourage users to engage with the business immediately.
Key Benefits for Local Businesses
- Drive Foot Traffic: By targeting users near their location, businesses like restaurants, salons, and retail stores can bring in more customers.
- Showcase Essential Information: Ads can display details like operating hours, reviews, and special promotions.
- Real-Time Updates: Businesses can update ads to reflect seasonal offers or changes in operating hours.
Example Use Case
A coffee shop runs a Local Ad targeting users within a 2-mile radius. When someone searches “coffee near me,” the ad appears, showing the shop’s address, hours, and a “Get Directions” link. This drives more in-store visits.
How Can Startups Leverage Google Ads to Build Brand Awareness?
Startups often struggle with limited brand recognition and need to generate awareness quickly in competitive markets.
Why is Google Ads Ideal for Startups?
Targeted Reach: Startups can focus on specific demographics, interests, or search queries to ensure ads reach the right audience.
Flexible Budgets: With no minimum spending requirement, startups can start small and scale their campaigns as they grow.
Customizable Campaigns: Google Ads allows startups to experiment with different campaign types, such as:
- Search Ads to capture high-intent users.
- Display Ads to build awareness through visuals.
Key Benefits for Startups
- Instant Visibility: Google Ads helps startups appear on the first page of search results, even when competing with established brands.
- Data-Driven Insights: Startups can track which campaigns perform best and refine their strategies.
- Build Credibility: Consistent ad visibility establishes trust and familiarity with potential customers.
Example Use Case
A tech startup offering a new project management tool runs Search Ads targeting keywords like “best project management software for teams.” This increases brand visibility among high-intent users looking for solutions.
Why Are B2B Services a Great Fit for Generating High-Value Leads?
B2B companies often focus on generating qualified leads rather than direct sales. These leads are typically decision-makers or stakeholders with high lifetime value.
Why is Google Ads Effective for B2B?
Precise Targeting: B2B companies can target users based on:
- In-market audiences (e.g., users actively researching business software or services).
- Demographics like job titles or company sizes.
Lead Generation Features: Google Ads offers tools like lead form extensions that allow users to submit contact details directly within the ad.
Key Benefits for B2B Services
- Efficient Lead Capture: Campaigns can focus on capturing contact details for follow-up.
- Scalable Solutions: Ads can be optimized to attract high-value clients.
- Measurable ROI: B2B services can track metrics like cost-per-lead (CPL) to evaluate the effectiveness of their campaigns.
Example Use Case
A digital marketing agency runs ads targeting “SEO services for small businesses.” The campaign uses lead form extensions to capture contact details, allowing the agency’s sales team to follow up with qualified leads.
How Does the Hospitality Industry Increase Bookings with Regional Targeting?
The hospitality industry relies heavily on regional and seasonal demand. For example, a hotel in a tourist destination may want to target travelers planning trips during peak seasons.
Why is Google Ads Effective for Hospitality?
Geo-Specific Campaigns: Advertisers can target users based on:
- Location (e.g., travelers in nearby cities or states).
- Search Intent (e.g., “hotels in Paris” or “cheap flights to Dubai”).
Promotional Opportunities: Hospitality businesses can showcase deals, packages, or special offers directly in their ads.
Key Benefits for the Hospitality Industry
- Increased Bookings: By targeting users searching for accommodations or travel-related services, businesses can drive direct bookings.
- Customized Messaging: Ads can highlight amenities, promotions, or unique selling points like “free breakfast” or “oceanfront views.”
- Multi-Platform Reach: Campaigns can appear on Search, Display, YouTube, and Maps, ensuring visibility across user touchpoints.
Example Use Case
A luxury hotel in Bali runs a regional campaign targeting users in Southeast Asia searching for “Bali vacation packages.” The ad highlights discounted rates for the upcoming holiday season, driving more bookings.
Google Ads Search Advertising benefits a wide range of industries and business types:
- E-Commerce Brands: Use Shopping Ads to visually promote products and drive online sales.
- Local Businesses: Leverage Local Ads to attract nearby customers and increase in-store visits.
- Startups: Build brand awareness quickly and efficiently with targeted, scalable campaigns.
- B2B Services: Generate high-value leads by targeting decision-makers and using lead generation tools.
- Hospitality Industry: Increase bookings by targeting travelers with regional and intent-based campaigns.
Each industry can customize Google Ads’ tools and features to suit its specific needs, making it one of the most versatile advertising platforms available.
How Flexible and Scalable is Google Ads?
Google Ads is designed to accommodate businesses of all sizes, offering unparalleled flexibility and scalability. Whether you’re a small business with a limited budget or a global enterprise, the platform provides tools and options to ensure your campaigns are cost-effective, adjustable, and performance-driven.
Is There a Minimum Budget Requirement to Run Campaigns?
One of Google Ads’ standout features is that it does not require advertisers to commit to a minimum budget to run campaigns.
This means that businesses can start advertising with whatever amount they’re comfortable spending, whether it’s $5 a day or $50,000 a month.
- Accessibility for Small Businesses: Small or local businesses with limited advertising budgets can start campaigns without financial pressure.
- Scalable for Larger Businesses: Enterprises can allocate substantial budgets to achieve massive reach and engagement without hitting any platform limits.
- Test-and-Optimize Approach: Businesses can start with a small budget to test campaign performance and scale up as they identify what works.
Daily and Lifetime Budget Options
- Advertisers can set either a daily budget (how much they want to spend per day) or a lifetime budget (the total amount to be spent over the campaign’s duration).
- Budgets are flexible and can be adjusted at any time based on performance and business goals.
How Does the Ad Rank System (Quality Score + CPC Bid) Ensure Cost-Efficient Ad Placements?
Google Ads uses an Ad Rank system to determine:
- Whether your ad will appear in search results.
- The position where your ad will be displayed.
Ad Rank is calculated using two key factors:
Quality Score: Google assigns a Quality Score to your ad, which is based on:
- Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR): How likely users are to click on your ad.
- Ad Relevance: How closely your ad matches the user’s search intent.
- Landing Page Experience: How useful and relevant your landing page is to users who click on your ad.
CPC Bid: This is the maximum amount you are willing to pay for a click on your ad. While advertisers set their maximum bid, the actual cost is determined by the ad auction, and you only pay slightly more than the next highest bid.
How Does Ad Rank Ensure Cost Efficiency?
Relevance is Rewarded: Ads with a high Quality Score are prioritized over ads with higher bids but lower relevance. This means advertisers don’t need to outbid competitors if their ads and landing pages are well-optimized.
Lower Costs for Better Ads: Higher-quality ads often pay less per click while still achieving higher placements. This encourages advertisers to focus on creating engaging and relevant ads.
Auction-Based Model: The ad auction ensures that advertisers only pay what is necessary to beat the competition. This prevents overspending.
Example:
Two advertisers are bidding for the same keyword:
- Advertiser A: CPC bid of $5 and a low Quality Score (3/10).
- Advertiser B: CPC bid of $3 but a high Quality Score (9/10).
Result: Advertiser B wins the auction and secures a higher ad placement despite a lower bid, thanks to a superior Quality Score.
Can Businesses Adjust Their Budgets in Real Time for Flexibility?
Yes, Budget Adjustments are Fully Flexible.
Google Ads allows advertisers to change their campaign budgets and bidding strategies at any time. This real-time flexibility ensures businesses can adapt their advertising spend based on performance, market trends, or changing business needs.
Key Flexibility Features
Increase or Decrease Budgets Anytime:
If a campaign is performing well, businesses can instantly increase their budget to maximize results.
If performance drops or priorities change, budgets can be scaled back or paused without penalties.
Real-Time Bidding Adjustments:
Advertisers can adjust their maximum bids for keywords, demographics, or geographic locations to focus spending on the most valuable opportunities.
Automated bidding strategies (e.g., Target CPA, Maximize Conversions) can also be updated based on changing goals.
Dayparting and Seasonal Adjustments:
Businesses can schedule ads to run only during specific times of the day or days of the week to optimize budget usage.
Seasonal campaigns can be launched with increased budgets and scaled down after peak periods.
Pause and Restart Campaigns:
Campaigns can be paused and restarted at any time, allowing businesses to control ad spend during low-demand periods or adjust strategies as needed.
Why Does This Matters?
Adapting to Performance: Businesses can quickly allocate more resources to high-performing campaigns or shut down underperforming ones.
Seasonal and Event-Based Flexibility: Retailers, for example, can ramp up budgets during holiday seasons or big sales events.
Efficient Spend Management: Advertisers only spend money when and where it makes the most sense, avoiding wasteful spending.
Example:
A restaurant runs a Google Ads campaign to promote a weekend brunch offer. On Saturday morning, they see strong performance and decide to increase their budget by 50% for the rest of the day to capitalize on the momentum. This flexibility ensures they maximize reach when it matters most.
Google Ads offers unmatched flexibility and scalability to businesses of all sizes through:
- No Minimum Budget Requirement:
- Advertisers can start with any budget, making it accessible to small businesses and scalable for enterprises.
- Ad Rank System:
- Combines Quality Score and CPC bids to ensure cost-effective ad placements, rewarding relevance and quality.
- Real-Time Budget Adjustments:
- Allows advertisers to adapt spending based on performance, trends, and seasonal demand.
These features make Google Ads a powerful platform for achieving advertising goals while maintaining full control over budgets and campaign strategies. Whether starting small or scaling big, Google Ads is built to grow alongside a business’s needs.
What Challenges Should Advertisers Be Prepared For?
While Google Ads is a powerful platform for driving traffic, generating leads, and increasing sales, it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for overcoming them and maximizing the effectiveness of campaigns. Let’s break them down:
Why Does High Competition in Some Industries Lead to Increased CPCs?
Certain industries, such as finance, legal, insurance, and e-commerce, are inherently more competitive because:
They have high customer lifetime values (CLVs), making each lead or conversion highly valuable.
Many advertisers bid on the same high-demand keywords to capture user attention.
The audience is often well-defined, so competitors are targeting the same group of users.
Impact on CPC (Cost-Per-Click)
High competition drives up keyword bidding prices during ad auctions because:
More advertisers are vying for the same top ad placements. Google prioritizes high-relevance, high-quality ads, so advertisers must either improve their Quality Score or bid higher to secure top positions.
Result: Increased CPCs, particularly for high-value keywords. For example:
Keywords like “personal injury lawyer” or “best insurance policy” can cost hundreds of dollars per click in some markets.
Why Is It a Challenge?
Budget Strain: Smaller advertisers may find it difficult to compete with larger businesses that have higher budgets.
Reduced ROI: Higher CPCs mean businesses must convert a greater percentage of clicks to justify the cost.
How to Overcome This Challenge?
Focus on Long-Tail Keywords:
Instead of bidding on high-cost, broad keywords, target long-tail keywords that have lower competition but still capture intent (e.g., “affordable personal injury lawyer in Chicago”).
Improve Quality Score:
Write highly relevant ad copy, select precise keywords, and optimize landing pages to increase Quality Score, which lowers CPC.
Leverage Niche Targeting:
Narrow down audiences based on demographics, locations, or interests to reduce competition and costs.
Adjust Bidding Strategies:
Use Target CPA or Maximize Conversions bidding to ensure ad spend is directed toward cost-efficient conversions.
What is the Learning Curve Like for New Advertisers on Google Ads?
Google Ads offers a wide range of tools, features, and settings that can overwhelm new advertisers. Challenges include:
Understanding Campaign Types: New advertisers must choose between search ads, display ads, shopping ads, and more, each with different goals and settings.
Keyword Research: Finding the right keywords and understanding match types (broad, phrase, exact) can be confusing.
Budget Management: Balancing daily budgets, bid adjustments, and ROI tracking requires careful planning.
Metrics and Analytics: Tracking and interpreting metrics like CTR, CPC, and ROAS can be daunting for beginners.
Ongoing Optimization: Campaigns require constant monitoring and tweaking to maintain performance, which can be challenging for those new to PPC.
Why Is It a Challenge?
Mistakes like bidding too high, targeting irrelevant audiences, or not optimizing landing pages can lead to wasted ad spend.
The complexity of the platform often requires a significant time investment to learn and master.
How to Overcome This Challenge?
1. Start with Simple Campaigns:
Use Smart Campaigns initially, which automate much of the setup process and require minimal manual management.
2. Leverage Google’s Resources:
Take advantage of free tools like Google Skillshop, which offers tutorials and certifications to help new advertisers understand the platform.
3. Experiment with Small Budgets:
Start with a modest budget to test campaign performance and learn without risking significant losses.
4. Use Pre-Built Tools:
Rely on tools like Keyword Planner and Performance Max Campaigns, which simplify keyword research and multi-channel reach.
5. Hire Experts or Agencies:
If the learning curve feels too steep, consider working with an experienced PPC agency or consultant.
How Does Ad Fatigue Impact Performance, and Why Do Ads Need Regular Updates?
Ad fatigue occurs when users repeatedly see the same ad and begin to ignore it. Over time, this leads to:
Reduced Engagement: Users stop clicking on the ad, leading to lower CTR.
Lower Conversion Rates: Even those who click may no longer engage with the product or service.
Decreased ROI: Campaigns become less effective, driving up the cost per conversion.
Why Does Ad Fatigue Happen?
Ads are shown to the same audience multiple times due to retargeting or narrow audience targeting.
Lack of variation in ad creatives (e.g., using the same headlines, descriptions, or images) makes them less appealing over time.
Why Is It a Challenge?
If advertisers don’t regularly refresh their campaigns, they risk diminishing returns on their ad spend.
Ad fatigue can also damage a brand’s perception if users find the ads repetitive or irrelevant.
How to Overcome This Challenge?
Refresh Ad Creatives Regularly:
Update headlines, descriptions, and images to keep the ads fresh and engaging. Test different value propositions or CTAs to see what resonates with your audience.
Use Responsive Ads:
Leverage Responsive Search Ads (RSA), which allow Google to test multiple combinations of headlines and descriptions automatically.
Rotate Ads:
Create multiple ad variations and use Google’s ad rotation settings to distribute impressions evenly across them.
Monitor Frequency:
Keep an eye on ad frequency to ensure users aren’t seeing the same ad too often.
Expand Audience Targeting!
Broaden audience segments to reach new users and reduce reliance on overexposed audiences.
Advertisers using Google Ads must be prepared to address the following challenges:
1. High Competition and Increased CPCs:
Focus on long-tail keywords, improve Quality Scores, and optimize bidding strategies to reduce costs in competitive industries.
2. Steep Learning Curve for New Advertisers:
Start simple, use available resources like Google Skillshop, and experiment with small budgets to minimize mistakes.
3. Ad Fatigue:
Regularly refresh creatives, monitor frequency, and use tools like Responsive Search Ads to maintain engagement and avoid diminishing returns.
Advertisers can optimize their campaigns, overcome common pitfalls, and achieve sustainable success with Google Ads.
What Emerging Trends Are Shaping Google Ads?
As the digital advertising landscape evolves, Google Ads continues to adapt by introducing new features and solutions to meet changing user behaviors, privacy regulations, and market demands. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends shaping the platform:
How Does Optimizing for Voice Search Create New Opportunities?
Voice search allows users to search the web by speaking their queries into devices like smartphones, smart speakers (e.g., Google Nest, Amazon Echo), or voice assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri).
It’s a growing trend, with an increasing number of users relying on voice commands for convenience and multitasking.
Why is Voice Search Important for Google Ads?
Voice search queries tend to be longer, more conversational, and question-based. For example:
- Typed query: “best restaurants near me”
- Voice query: “What are the best restaurants near me for dinner?”
Increased Adoption of Smart Devices:
With the rise of smart speakers and voice-enabled devices, advertisers can reach users in new contexts, such as while driving or cooking.
Localized Intent:
Voice searches often have strong local intent, making them valuable for businesses targeting nearby customers.
How Advertisers Can Optimize for Voice Search?
Focus on Long-Tail Keywords:
Incorporate natural, conversational phrases and question-based keywords into campaigns (e.g., “Where can I buy organic vegetables?”).
Use Location Targeting:
Optimize campaigns for local intent by using geographic targeting and keywords like “near me” or “in [city].”
Leverage Structured Data:
Ensure your website has structured data markup to improve visibility in featured snippets or voice search results.
Create Mobile-Friendly Landing Pages:
Since many voice searches happen on mobile devices, ensure your landing pages are fast and mobile-optimized.
Incorporate FAQ Content:
Develop content that answers common voice search questions to align with user intent.
Example Use Case:
A local coffee shop can target voice search users with ads using keywords like “Where’s the closest coffee shop?” or “Best coffee near me,” ensuring they appear when someone asks a voice assistant for recommendations.
What is the Privacy Sandbox, and How is Google Adapting to a Cookieless Future?
The Privacy Sandbox is Google’s initiative to enhance user privacy while maintaining a healthy online advertising ecosystem. It focuses on replacing third-party cookies with privacy-preserving alternatives for tracking and targeting users.
Third-party cookies are being phased out in Google Chrome (following other browsers like Safari and Firefox) as part of the industry’s response to growing concerns over user privacy.
Why is the Privacy Sandbox Important for Google Ads?
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter data privacy regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the US.
Impact on Ad Targeting:
Third-party cookies have been a primary method for tracking user behavior across websites, enabling advertisers to create highly targeted campaigns. With their removal, advertisers need new ways to reach audiences effectively.
Maintaining User Trust:
Google aims to balance user privacy with advertisers’ needs by introducing privacy-first alternatives.
Key Privacy Sandbox Solutions
Topics API:
Replaces cookies by assigning users to broad interest categories (e.g., “Fitness” or “Travel”) based on their recent browsing activity. Advertisers can target these topics instead of individual user data.
FLEDGE (First Locally-Executed Decision over Groups Experiment):
Allows interest-based ad retargeting without exposing individual user data to advertisers.
Attribution Reporting API:
Tracks ad performance (e.g., clicks and conversions) without relying on user-specific data.
How Advertisers Can Prepare for the Cookieless Future?
Focus on First-Party Data:
Collect and use first-party data (e.g., email addresses, purchase history) to create custom audiences and build retargeting lists.
Leverage Google’s Privacy Tools:
Use tools like Customer Match and audience segments to reach users effectively while complying with privacy standards.
Adopt Contextual Targeting:
Shift focus to targeting based on the content of web pages (e.g., displaying ads for hiking gear on outdoor-related blogs).
Invest in AI and Automation:
Rely on Google Ads’ machine learning algorithms to optimize campaigns and fill the gaps left by cookies.
Example Use Case:
A clothing retailer uses Customer Match to upload its customer email list, enabling personalized targeting without relying on third-party cookies. This approach ensures compliance while maintaining campaign effectiveness.
How Can Advertisers Align Campaigns with Sustainability Metrics?
Consumers and businesses are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, with many choosing brands that demonstrate environmental responsibility.
Google is integrating sustainability metrics and features into its advertising platform to help businesses align with user preferences and global trends.
How is Google Supporting Sustainable Advertising?
Carbon Footprint Transparency:
Google Ads provides data on the carbon emissions generated by ad campaigns, allowing advertisers to understand and reduce their environmental impact.
Green Certifications:
Advertisers can promote their eco-friendly practices by showcasing certifications or using “sustainability” as a value proposition in their ads.
Eco-Friendly Campaign Targeting:
Advertisers can target users interested in sustainability or environmentally friendly products by leveraging affinity or in-market audience segments.
How Advertisers Can Align Campaigns with Sustainability Metrics?
Highlight Green Initiatives:
Include messaging in ads about sustainability efforts, such as using renewable energy, reducing waste, or offering eco-friendly products.
Partner with Green Platforms:
Ensure ads run on platforms and publishers that align with sustainable practices.
Optimize Ad Performance:
Reduce wasted spend and impressions by improving targeting accuracy, which indirectly lowers the environmental impact of campaigns.
Why Sustainability Matters for Advertisers?
Builds Brand Loyalty:
Consumers are more likely to support brands that align with their values, including environmental consciousness.
Differentiates the Brand:
Highlighting sustainability can help businesses stand out in competitive markets.
Aligns with Google’s Vision:
Google has committed to becoming carbon-free by 2030, making sustainability a core focus across its services.
Example Use Case:
An outdoor gear brand emphasizes its use of recycled materials in its ad copy. Using in-market audiences for “environmentally conscious consumers,” the brand targets users interested in sustainability, driving both engagement and conversions.
The advertising landscape is evolving, and Google Ads is adapting through these key trends:
- Voice Search Optimization: Opens opportunities for businesses to target conversational and localized queries.
- Privacy Sandbox: Prepares advertisers for a cookieless future by introducing privacy-first solutions like Topics API and FLEDGE.
- Sustainability Metrics: Encourages brands to align with environmentally conscious practices, appealing to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Advertisers can future-proof their campaigns, remain competitive, and connect meaningfully with their audiences, by staying ahead of these trends.
How Does Google Ads Distinguish Itself From Platforms Like Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads) or Amazon Advertising?
Google Ads stands out from competitors due to its vast reach, advanced targeting options, and extensive ecosystem. Let’s break it down:
Comparison with Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads)
Search Market Share:
Google dominates the global search engine market, accounting for approximately 92% of all searches, compared to Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads), which holds around 3-4%.
Google Ads reaches a much larger audience, making it ideal for businesses targeting mass-market or global users.
Ad Network and Ecosystem:
Microsoft Advertising extends beyond Bing to include Yahoo and AOL, but its network is smaller than Google’s.
Google Ads integrates with a broader ecosystem, including YouTube, Google Display Network, Gmail, and Google Maps, offering multi-channel opportunities.
Targeting and Data:
Google Ads benefits from unparalleled user data collected across its platforms, enabling more precise audience targeting.
Microsoft Advertising’s targeting options are improving but are not as extensive as Google’s (e.g., fewer audience segments and demographic options).
Advantages of Google Ads Over Microsoft Advertising:
- Larger Reach: Advertisers can access a global audience across diverse devices and platforms.
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Google’s AI-powered bidding strategies (e.g., Target CPA, ROAS) are more refined.
- Innovative Features: Tools like Performance Max Campaigns and Responsive Search Ads provide flexibility and optimization capabilities that are not as advanced in Microsoft Advertising.
When to Use Microsoft Advertising?
Microsoft Advertising can be valuable for targeting niche audiences or professionals, as Bing users tend to skew older and more affluent. It’s also cost-effective due to less competition, resulting in lower CPCs.
For detailed information on Microsoft Advertising and its features, visit the Microsoft Advertising Help Center.
Comparison with Amazon Advertising
Ad Context:
Amazon Advertising focuses exclusively on shopping and e-commerce, targeting users within the Amazon ecosystem.
Google Ads targets users at various stages of the buying journey, from awareness to purchase, across multiple platforms.
Audience Intent:
Amazon Ads targets purchase-ready consumers already on Amazon, searching for specific products.
Google Ads targets high-intent audiences both in and outside of the shopping phase, making it suitable for e-commerce, lead generation, and brand awareness.
Ad Types:
Amazon primarily offers Sponsored Product Ads, Display Ads, and Video Ads focused on product listings.
Google Ads offers a broader range of campaigns, including:
- Shopping Ads (similar to Amazon).
- Search Ads, Display Ads, YouTube Ads, and Local Ads, reaching users in various contexts.
Advantages of Google Ads Over Amazon Advertising:
- Broader Audience Reach: Google Ads captures users across multiple platforms and stages of their buying journey, not just those already on Amazon.
- Diverse Campaign Goals: Advertisers can use Google Ads for e-commerce, lead generation, or brand-building, while Amazon is limited to product sales.
- Flexibility for Non-E-Commerce Businesses: Google Ads supports businesses that aren’t selling physical products, such as services, software, or local businesses.
When to Use Amazon Advertising?
Amazon is ideal for e-commerce brands looking to target users already ready to buy. It’s best for product-centric campaigns within Amazon’s ecosystem.
Why is Google Ads Particularly Effective for High-Intent Audiences Compared to TikTok Ads?
Google Ads and TikTok Ads serve different purposes, targeting audiences with varying levels of intent. Here’s how Google Ads stands out for high-intent users:
Audience Behavior and Intent
Google Ads:
Targets users actively searching for solutions, products, or services. These users are often closer to making a decision or purchase.
Example: Someone searching “best smartphones under $500” has a clear intent to buy soon.
TikTok Ads:
Focuses on entertainment-driven discovery. TikTok users are scrolling through videos and may not have immediate purchase intent.
Ads on TikTok are typically shown to users passively engaging with content, making it more effective for brand awareness or impulse buys rather than high-intent conversions.
Ad Targeting and Placement
Google Ads:
Leverages keyword targeting, which directly matches user queries to advertiser offerings.
Appears in contexts where users are looking for specific answers or products (e.g., Google Search, YouTube, or Shopping results).
TikTok Ads:
Uses audience-based targeting (e.g., interests, demographics) rather than search intent.
Ads appear in-feed, often as part of the user’s entertainment experience, which may result in lower click-through or conversion rates for high-intent goals.
Ad Goals and Use Cases
Google Ads:
Best for driving direct actions, such as website visits, lead submissions, or purchases, due to the high intent of its audience.
Suitable for businesses across industries (e.g., e-commerce, local services, B2B).
TikTok Ads:
Ideal for brand storytelling, viral campaigns, or product awareness among younger audiences.
Works well for impulse purchases or products with strong visual appeal.
Performance Metrics
Google Ads:
Focuses on measurable, action-oriented metrics like CTR, conversion rate, and ROAS.
Advertisers have access to real-time data and advanced attribution models to track performance.
TikTok Ads:
Metrics often center around reach, engagement, and impressions, which are better suited for awareness campaigns rather than direct conversions.
Example Use Case Comparison
Google Ads: A home repair service targeting users searching for “emergency plumber near me” can directly reach high-intent users ready to book a service.
TikTok Ads: A beauty brand promoting a trending skincare product might create an entertaining, viral campaign targeting users who aren’t actively searching for skincare but might buy impulsively.
Google Ads distinguishes itself from competitors through its ability to target high-intent users across a vast ecosystem. Here’s how it compares:
- Microsoft Advertising:
- Google Ads offers broader reach, more advanced tools, and a larger audience base.
- Microsoft Advertising is useful for niche audiences with lower competition.
- Amazon Advertising:
- Google Ads supports broader campaign goals, while Amazon focuses solely on e-commerce within its ecosystem.
- Google captures users earlier in the buying journey, making it more versatile.
- TikTok Ads:
- Google Ads is more effective for high-intent actions, while TikTok is better for discovery and brand awareness.
By understanding these distinctions, businesses can leverage Google Ads for direct, measurable results and complement it with other platforms for broader marketing strategies.
Why Should Businesses Consider Google Ads?
Google Ads is a versatile and powerful platform that caters to the needs of local businesses, e-commerce brands, and global enterprises. Its unique features, robust ecosystem, and adaptability make it a top choice for advertisers aiming to drive results at any scale.
How Does Google Ads Cater to the Needs of Local Businesses, E-Commerce Brands, and Global Enterprises Alike?
For Local Businesses
Why Is It Ideal?
Local businesses, such as restaurants, salons, and repair services, rely heavily on nearby customers. Google Ads provides hyperlocal targeting tools to reach audiences based on location and intent.
Key Features:
Geographic Targeting:
- Businesses can target specific areas, zip codes, or a defined radius around their location.
- Example: A bakery targeting users within a 5-mile radius who search for “best cakes near me.”
Local Ads:
- These ads appear on Google Maps, Search, and partner platforms, encouraging users to visit physical locations or call directly.
- Features like call extensions and location extensions make it easy for customers to take immediate action.
Local Service Ads:
Designed specifically for service-based businesses, these ads help businesses showcase customer reviews, business hours, and contact information to attract high-intent leads.
Why It Works!
Local businesses benefit from Google’s ability to capture high-intent searches like “plumber near me” or “grocery store open now,” which drive immediate foot traffic, calls, or appointments.
For E-Commerce Brands
Why Is It Ideal?
E-commerce brands thrive on visibility and conversions, and Google Ads offers specialized tools like Shopping Ads and Performance Max Campaigns to meet their needs.
Key Features:
Shopping Ads:
Product-specific ads that include images, prices, and product details, displayed prominently in search results and the Shopping tab.
Example: A clothing retailer uses Shopping Ads to showcase winter jackets with pricing and store information when users search for “buy winter jackets online.”
Dynamic Remarketing:
Re-engage users who have visited the website but didn’t complete a purchase by showing personalized ads featuring the exact products they viewed.
Global Reach:
Google Ads supports campaigns targeting audiences worldwide, helping e-commerce brands expand into new markets.
Smart Campaigns:
Automated campaigns optimized for conversions, simplifying the process for e-commerce stores with limited resources.
Why Does It Work?
Google Ads captures users at multiple stages of the buying journey—whether they’re searching for a product, comparing prices, or ready to buy. Its ability to show product details and images increases conversion rates.
For Global Enterprises
Why Is It Ideal?
Global enterprises need scalable solutions to manage massive campaigns, reach diverse markets, and maintain brand consistency across regions.
Key Features:
Advanced Audience Targeting:
Enterprises can segment their audiences based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and even specific markets or languages.
Example: A luxury car brand targets affluent individuals in specific countries with ads highlighting exclusive models.
Multi-Campaign Management:
Google Ads’ tools, like Campaign Manager 360, allow enterprises to manage multiple campaigns across regions while tracking performance at a granular level.
Cross-Platform Reach:
Ads can appear on Google Search, YouTube, Gmail, and the Google Display Network, ensuring enterprises can engage users across platforms and devices.
Customizable Budgets and Scaling:
Enterprises can allocate large budgets strategically across different campaigns and adjust them in real-time based on market performance.
Why Does It Work?
Google Ads’ extensive ecosystem ensures global enterprises can maintain consistent messaging while adapting to the specific needs of local markets, enabling both scale and precision.
What Makes it Possible to Create Tailored Campaigns for Success?
Google Ads offers a wide array of customization options, allowing businesses to create highly tailored campaigns that align with their goals, audience, and market conditions.
Customizable Campaign Types
- Search Ads: Target users searching for specific keywords.
- Display Ads: Reach audiences with visually appealing ads across Google’s Display Network.
- Shopping Ads: Showcase products to users ready to buy.
- YouTube Ads: Leverage video content to build brand awareness or drive direct actions.
- Performance Max Campaigns: Automate multi-channel advertising to maximize results with minimal manual effort.
Granular Targeting Options
Keyword Targeting: Match ads to user queries based on intent (broad, phrase, or exact match).
Audience Segmentation:
- Target users based on demographics, interests, or behaviors.
- Use in-market audiences for high-intent users actively researching products or services.
Geographic and Language Targeting: Focus on specific regions, cities, or even languages to reach the right audience.
Ad Extensions for Personalization
- Sitelink Extensions: Direct users to specific pages on a website (e.g., “Shop Now” or “Learn More”).
- Callout Extensions: Highlight unique features like “Free Shipping” or “24/7 Support.”
- Price Extensions: Showcase pricing for products or services directly in the ad.
Landing Page Optimization
Google Ads campaigns can be paired with optimized landing pages that match the ad content, ensuring a seamless user experience and higher conversion rates.
AI-Powered Automation
Tools like Smart Bidding, Responsive Search Ads, and Performance Planner use AI to optimize campaigns, ensuring businesses get the best results for their investment.
How Can Businesses Leverage the Ecosystem of Tools and Integrations to Engage the Right Audience at the Right Time?
Google Ecosystem Advantage
Google Ads integrates seamlessly with other tools in the Google ecosystem, enhancing campaign performance and insights:
Google Analytics 4 (GA4):
Tracks user behavior across websites and apps, providing deeper insights into ad performance and customer journeys.
Google Tag Manager (GTM):
Simplifies tracking setup for conversions, events, and user interactions without needing extensive technical expertise.
YouTube:
Allows businesses to engage with users via video ads, targeting both awareness and direct action campaigns.
Google Display Network:
Extends reach by displaying ads on millions of partner websites and apps.
Third-Party Integrations
Google Ads supports integrations with popular CRMs like HubSpot and Salesforce, enabling businesses to:
- Automate lead management and nurturing.
- Use customer data to create custom audiences and retarget effectively.
Real-Time Performance Monitoring
- The Google Ads dashboard provides real-time metrics, including impressions, clicks, conversions, and ROAS (Return on Ad Spend).
- Advertisers can make instant adjustments to budgets, targeting, and ad creatives based on performance data.
Scalable Features
- Google Ads supports campaigns of any size, from small local businesses to global enterprises, allowing advertisers to scale their efforts as they grow.
- Automated tools like Smart Campaigns and Performance Max reduce complexity, making it easy for businesses to expand their reach.
Google Ads caters to the needs of local businesses, e-commerce brands, and global enterprises by offering:
- Flexibility: Tailored campaign types and granular targeting options to suit specific business goals.
- Advanced Tools: An integrated ecosystem (GA4, GTM, and CRMs) that simplifies workflows and enhances campaign insights.
- Scalability: A platform that accommodates businesses of all sizes, allowing them to adjust budgets and campaigns in real time.
Businesses can engage the right audience at the right time, ensuring their marketing efforts drive measurable results, by leveraging Google Ads.
Want SEO Consultancy for your project?
If you feel that you are lost in somewhere middle, I am here to help you with this.
Table of Contents
Toggle