How can you ensure a seamless online experience while navigating through the complexities of implementing 301 redirects?
Are you prepared to tackle challenges such as traffic loss, slower page load times, and potential SEO risks head-on?
With strategic planning and execution, can you optimize your website to maximize effectiveness and user satisfaction?
In the big online world, think of websites like growing plants, always changing and adapting.
Sometimes they need to change addresses, just like when you move to a new house.
But what happens to the people looking for your old place?
That’s where 301 redirects come in – they’re like secret passages that guide visitors and search engines to the right spot.
Let’s take a closer look at these 301 redirects.
They’re basically signs that say, “Hey, we’ve moved permanently!”
Simple, right?
But they’re more than just signs – they’re the glue that holds websites together during changes.
We’ll find out how to keep an eye on these redirects, making sure they’re still doing their job right.
So, let’s learn in this guide how to deal with 301 redirects!
What are 301 Redirects?
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from one URL to another. It informs search engines and web browsers that the requested page has permanently moved to a new location.
The primary purpose of a 301 redirect is to ensure a seamless user experience by automatically redirecting visitors from old or outdated URLs to the corresponding, updated ones.
Let’s understand it with simple way.
Imagine you have a favorite store you always visit, but one day you find out it moved to a new location. Now, instead of shutting down and disappearing, the store puts up a sign directing you to its new spot.
That’s exactly what a 301 redirect does online.
It’s like a signpost that tells your web browser, “Hey, the page you’re looking for has moved permanently to a new address.”
So, when you type in the old URL or click on an old link, the 301 redirect automatically sends you to the new location, ensuring you still find what you’re looking for without any hassle.
How 301 Redirects Work?
When a user or search engine crawler attempts to access a URL that has been redirected with a 301 status code, the server sends an HTTP response indicating that the requested page has moved permanently.
The browser or search engine then automatically follows the redirect to the new URL specified in the redirect directive.
This process ensures that both users and search engines are directed to the correct page without encountering errors or broken links.
Key Differences Between 301, 302, and Other Redirects?
While 301 redirects are permanent, there are other types of redirects, such as 302 (temporary) redirects and meta refresh redirects.
Understanding the differences between these redirect types is crucial for implementing the most appropriate redirect strategy for your website.
Unlike 301 redirects, which transfer the SEO value and ranking power of the original URL to the new one, 302 redirects are temporary and do not pass on link equity. Similarly, meta refresh redirects are executed at the HTML level and may not be as effective for SEO purposes as server-side redirects like 301s.
Therefore, choosing the right redirect type depends on factors such as the permanence of the URL change and its impact on SEO.
When to Use 301 Redirects?
Knowing when to employ 301 redirects is crucial for maintaining a seamless user experience and preserving SEO equity during website changes.
There may be some specific scenarios where implementing 301 redirects are essential to ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct pages.
There are four major reasons that you may face:
- Website Restructuring or Redesign
- URL Changes
- Handling Broken links and Error Pages
- Migrating to a new Domain or Subdomain
Let’s understand each of these circumstances one by one.
1. Website Restructuring or Redesign:
During a website restructuring or redesign, URLs often change to improve site navigation, update content organization, or enhance user experience.
Implementing 301 redirects allows you to seamlessly redirect visitors from old URLs to their corresponding new locations.
This will prevent disruptions in traffic and preserving SEO rankings accumulated over time.
2. URL Changes:
URL changes may occur for various reasons, such as:
- Optimizing for SEO
- Improving readability
- Aligning with new content strategies.
When URLs are modified, implementing 301 redirects ensures that visitors accessing the old URLs are automatically redirected to the new ones.
This helps maintain consistency in website navigation and prevents users from encountering broken links or error pages.
3. Handling Broken Links and Error Pages:
Broken links and error pages can negatively impact user experience and SEO efforts.
You can redirect traffic from broken links or error pages to relevant, functioning pages on your website by applying 301 redirects.
This not only prevents users from encountering dead ends but also preserves SEO value by consolidating link equity and ensuring that search engines can crawl and index the redirected pages.
4. Migrating to a New Domain or Subdomain:
When migrating to a new domain or subdomain, implementing 301 redirects is essential for seamlessly transferring traffic and preserving SEO rankings.
You can ensure that visitors who access the old domain or subdomain are automatically redirected to the new one by setting up redirects from the old URLs to the corresponding new ones.
This minimizes the impact of the migration on user experience and helps maintain the website’s visibility and authority in search engine rankings.
How to Implement 301 Redirects?
Once you understand the importance of 301 redirects, the next step is to implement them effectively.
Perfectly implementation will ensure seamless website navigation and maintain SEO integrity during URL changes or site migrations.
Let’s learn the various methods and best practices for implementing 301 redirects.
Using Content Management Systems
Here are a few Content Management Systems (CMS) that offer features or plugins/extensions for managing redirects:
- WordPress: WordPress is one of the most popular CMS platforms, and it offers several plugins for managing redirects, such as “Redirection” , “Yoast SEO” and “RankMath”.
- Drupal: Drupal is another widely used CMS known for its flexibility and robustness. Modules like “Redirect” in Drupal allow users to set up and manage redirects easily.
- Joomla: Joomla is a user-friendly CMS that also provides extensions for managing redirects, such as “SH404SEF” and “Redirect Manager.”
- Magento: Magento is a popular CMS for e-commerce websites. It offers extensions like “SEO Suite Ultimate” that include features for managing redirects.
- Shopify: Shopify is a leading e-commerce platform that provides built-in tools for managing redirects, allowing users to set up URL redirects directly from the admin dashboard.
These CMS platforms offer various options for managing redirects, catering to different user preferences and requirements.
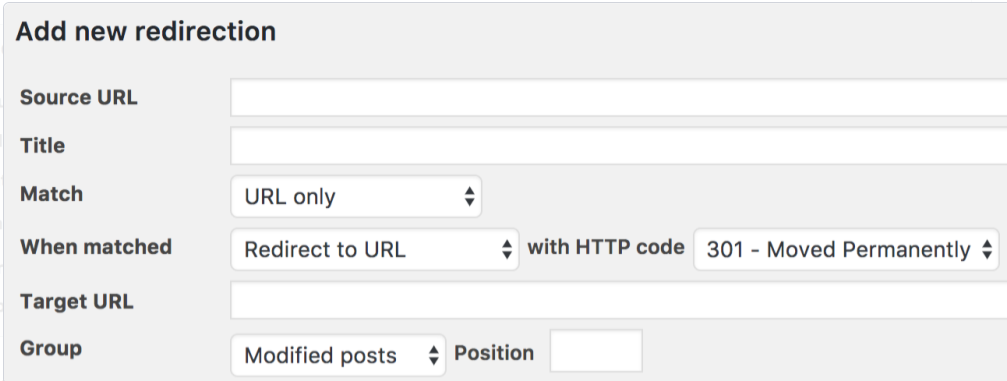
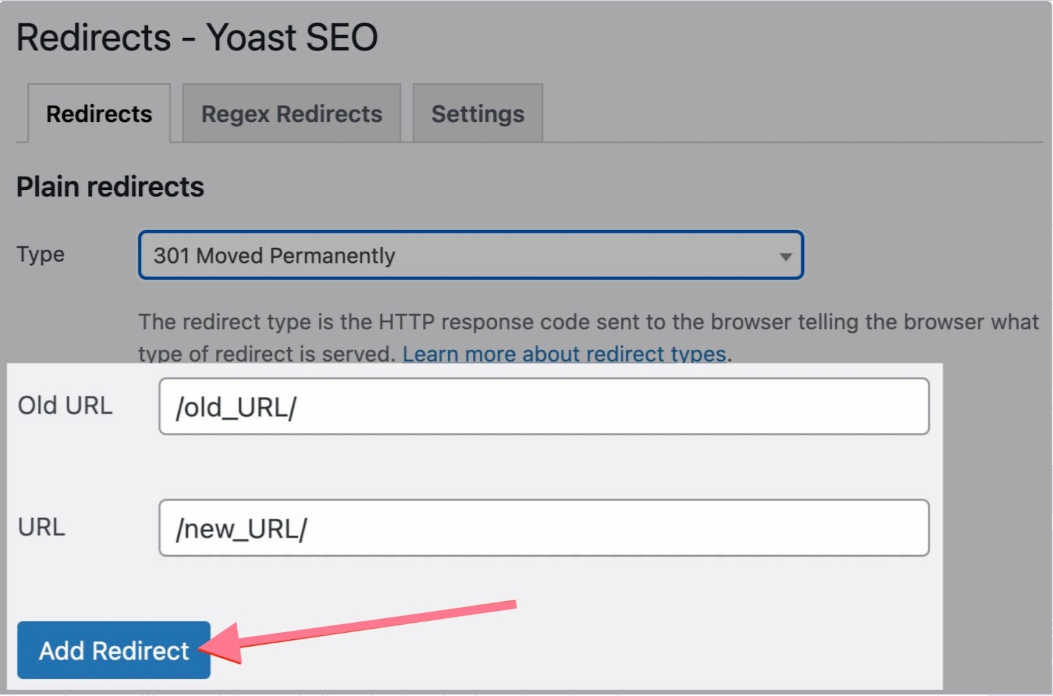
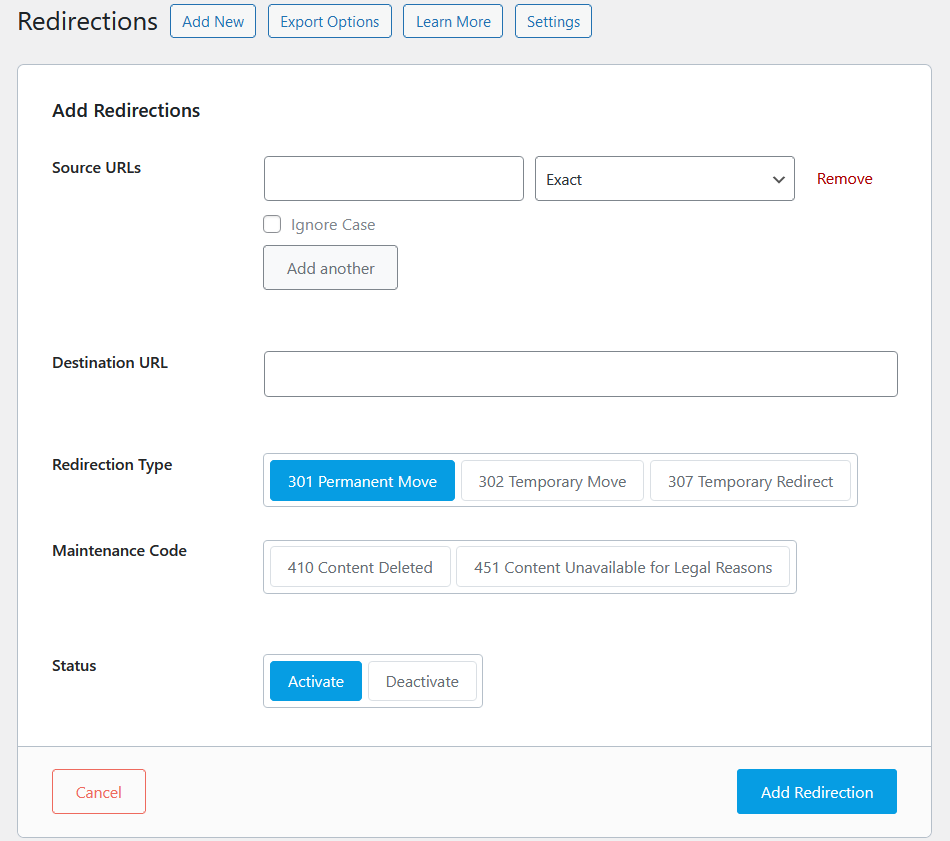
301 Redirects using WordPress Plugins
Managing websites can be tricky, especially when it comes to changing URLs. Luckily, WordPress has handy tools like ‘Redirection,’ ‘Yoast SEO,’ and ‘RankMath’ plugins to help with that.
These tools make it easy to keep your site organized and ensure that when a link changes, visitors still find what they’re looking for.
Let’s take a closer look at how these plugins make handling URL changes a breeze for WordPress users.”
Configuring Redirects in Nginx Server:
Similarly, for websites hosted on Nginx servers, redirect configurations can be managed directly within the server configuration file.
Nginx provides directives like “rewrite” to specify 301 redirects, allowing webmasters to control URL redirections efficiently.
This approach is ideal for Nginx users familiar with server configuration and looking for a robust method to implement redirects.
Using Content Management Systems (CMS) for Redirects
Content Management Systems (CMS) offer user-friendly interfaces and plugins/extensions that simplify the process of implementing 301 redirects without requiring manual server configuration.
Users can leverage built-in features or install plugins/extensions specifically designed for managing redirects within the CMS platform.
This method is suitable for website owners who prefer a more accessible and intuitive approach to redirect management.
SEO Implications of 301 Redirects
Implementing 301 redirects can have significant implications for a website’s search engine optimization (SEO) performance.
Let’s explore how 301 redirects impact SEO and provides insights into:
- Preserving Link equity
- Preventing duplicate content issues
- Understanding their effect on search engine rankings
- Avoiding common mistakes
These could undermine SEO benefits. Let’s learn!
Preserving Link Equity and SEO Value
When implementing 301 redirects, preserving link equity is crucial for maintaining the SEO value of redirected URLs.
This involves ensuring that incoming links pointing to the original URL pass on their ranking power to the destination URL.
Webmasters can consolidate link equity from redirected pages, strengthening the overall SEO performance of the website and preserving its authority in search engine results by properly implementing 301 redirects.
Here’s an example illustrating how preserving link equity and SEO value works with 301 redirects:
Let’s say you have a blog post on your website titled “Top 10 Tips for Healthy Eating” that has gained a lot of backlinks from reputable health websites over time.
However, you’ve decided to update the URL structure of your website, and the URL for this blog post will change from:
Old URL: https://www.example.com/blog/top-10-tips-for-healthy-eating
to
New URL: https://www.example.com/nutrition/top-10-tips-for-healthy-eating
Now, if you were to simply change the URL without setting up a redirect, anyone clicking on the old URL or following a backlink to the old URL would encounter a 404 error, indicating that the page doesn’t exist.
This not only leads to a poor user experience but also wastes the SEO value of those backlinks.
However, by implementing a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new URL, you can preserve the link equity and SEO value of those backlinks. When a user or search engine crawler follows a backlink to the old URL, the 301 redirect will automatically redirect them to the new URL, ensuring that they still reach the intended content.
As a result, the SEO authority passed through those backlinks is retained, and your new URL inherits the ranking power accumulated by the old URL.
This helps maintain or even improve your website’s search engine rankings for relevant keywords, ultimately contributing to the overall SEO health and visibility of your website.
Preventing Duplicate Content Issues
Redirecting multiple URLs to a single destination can inadvertently create duplicate content issues if search engines perceive the redirected URLs as separate pages with identical or similar content.
To prevent duplicate content issues, webmasters should implement 301 redirects correctly and ensure that redirected URLs are canonicalized to the preferred version.
Canonicalization helps search engines understand the primary URL for indexing purposes, mitigating the risk of duplicate content penalties and preserving SEO integrity.
Here’s an example illustrating how canonicalization helps prevent duplicate content issues:
Let’s say you run an e-commerce website selling sports shoes, and you have product pages for different colors of the same shoe model.
For example, you have product pages for “Nike Air Zoom Pegasus – Black” and “Nike Air Zoom Pegasus – White.”
However, both product pages contain almost identical content, except for the color variation.
Without proper canonicalization, search engines may interpret these similar product pages as duplicate content, potentially resulting in lower rankings or penalties in search results.
To prevent this issue, you can implement canonical tags on these product pages.
In this example, you would add a canonical tag pointing to the preferred version of the page, typically the main product page.
Here’s how you might implement canonicalization in the HTML code for the “Nike Air Zoom Pegasus – Black” product page:
<head><title>Nike Air Zoom Pegasus - Black</title>
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/products/nike-air-zoom-pegasus" />
</head>In this example, the canonical tag tells search engines that the preferred version of the page is the main product page (https://www.example.com/products/nike-air-zoom-pegasus), regardless of the color variation.
As a result, search engines understand that both the black and white versions of the shoe are essentially the same product, preventing duplicate content issues.
By implementing canonicalization effectively, you ensure that search engines consolidate ranking signals for similar pages and attribute authority to the preferred version, ultimately improving the SEO performance of your website while avoiding duplicate content penalties.
Impact on Search Engine Rankings
The implementation of 301 redirects can have both immediate and long-term effects on search engine rankings.
While 301 redirects pass on the majority of link equity from the original URL to the destination URL, there may be a temporary fluctuation in rankings as search engines re-crawl and reindex the redirected pages.
However, if implemented correctly, 301 redirects can help maintain or even improve search engine rankings by consolidating authority and ensuring that users are directed to relevant content.
Common Mistakes to Avoid for SEO Benefits
Despite their benefits, improper implementation of 301 redirects can lead to SEO pitfalls that undermine their effectiveness.
Common mistakes to avoid include implementing redirects incorrectly, creating redirect chains or loops, failing to update internal links and sitemaps, and neglecting to monitor and maintain redirects over time.
Here I am explaining these few common mistakes to avoid for SEO benefits:
- Incorrect Redirect Implementation: Implementing redirects incorrectly, such as using 302 redirects instead of 301 redirects for permanent URL changes, can lead to loss of SEO value and indexing issues.
- Redirect Chains and Loops: Allowing redirect chains or loops to occur can impact site speed and crawl efficiency, leading to poor user experience and potential SEO penalties.
- Failure to Update Internal Links and Sitemaps: Neglecting to update internal links and XML sitemaps after implementing redirects can result in broken links and indexing issues, negatively affecting SEO performance.
- Overuse of Redirects: Using excessive redirects, especially unnecessary redirects for every URL change, can increase page load times and confuse search engines, potentially harming SEO rankings.
- Lack of Regular Redirect Auditing and Maintenance: Failing to regularly audit and maintain redirects can result in outdated or broken redirects, leading to lost traffic, decreased user experience, and diminished SEO performance over time.
- Incorrect Handling of URL Parameters: Mishandling URL parameters, such as allowing multiple variations of the same content to be indexed or failing to set canonical tags, can result in duplicate content issues and dilution of SEO authority.
- Not Leveraging Redirects for Site Structure Optimization: Missing opportunities to use redirects for site structure optimization, such as consolidating similar pages or redirecting outdated content to relevant pages, can limit SEO improvements and user experience enhancements.
Avoiding these common mistakes and following best practices for implementing and managing redirects can help website owners maximize the SEO benefits of their redirect strategies. This ensures they maintain optimal website performance in search engine rankings.
Monitoring and Managing 301 Redirects
Once 301 redirects are implemented, it’s crucial to monitor and manage them effectively to ensure they continue to serve their intended purpose.
Let’s explore various tools and techniques for monitoring redirects, addressing issues such as redirect chains and loops.
Tools and Techniques for Monitoring Redirects
Monitoring redirects is essential to ensure they are functioning as intended and to identify any potential issues promptly.
There are several tools and techniques available for monitoring redirects, including web analytics platforms, server log analysis, and specialized redirect monitoring tools.
Here are a few these tools and techniques for monitoring redirects:
- Google Search Console: GSC provides a “Crawl Errors” report that includes information about crawl errors encountered by Google when crawling your website, including any issues with redirects.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Screaming Frog is a powerful SEO tool that can crawl websites and identify issues with redirects, including redirect chains, loops, and missing redirects.
- SEMRush: SEMRush offers a suite of SEO tools, including a Site Audit feature that can identify redirect issues and provide recommendations for improvement.
- Redirect Checker Tools: Various online tools, such as Redirect Checker by Ahrefs or Redirect Checker by SmallSEOTools, allow you to input a URL and check the HTTP status code returned, helping identify any redirect issues.
- Server Logs Analysis: Analyzing server logs can provide insights into how redirects are being handled by your server, including information about the number of redirects, redirect paths, and any errors encountered.
- Browser Developer Tools: Most modern web browsers come with built-in developer tools that allow you to inspect network requests and view HTTP headers, making it possible to monitor redirects in real-time as you browse the web.
These tools and techniques can help website owners and SEO professionals effectively monitor redirects, identify issues, and optimize redirect configurations for improved website performance and user experience.
Handling Redirect Chains and Loops
Redirect chains and loops occur when a series of redirects lead to multiple intermediary URLs before reaching the final destination.
Or when redirects inadvertently create a loop by redirecting back to a previously visited URL.
Both scenarios can impact user experience and SEO performance by increasing page load times and confusing search engine crawlers.
To address redirect chains and loops, webmasters should regularly audit redirect configurations, consolidate multiple redirects into a single redirect when possible, and ensure that redirects are implemented correctly to prevent unintended loops.
Here’s an example illustrating how to handle redirect chains and loops:
Let’s say you have a website where the old URL structure has been redesigned, resulting in multiple redirect chains and a redirect loop.
Redirect Chain Example:
- Old URL: https://www.example.com/old-category/old-page
- Redirects to: https://www.example.com/new-category/new-page
- Redirects to: https://www.example.com/new-category/new-page-final
In this example, the old URL (/old-category/old-page) is redirected twice before reaching the final destination (/new-category/new-page-final).
Each redirect in the chain introduces additional latency and potential points of failure, which can negatively impact user experience and SEO performance.
Redirect Loop Example:
- Old URL: https://www.example.com/old-page
- Redirects to: https://www.example.com/new-page
- Redirects back to: https://www.example.com/old-page
In this example, the old URL (/old-page) is redirected to the new page (/new-page), but then the new page redirects back to the old URL, creating a loop.
This loop can cause browsers and search engine crawlers to get stuck in an infinite loop, resulting in crawl errors and indexing issues.
To handle redirect chains and loops effectively, it’s essential to:
- Minimize Redirect Chains: Whenever possible, consolidate multiple redirects into a single redirect to reduce latency and potential points of failure.
- Resolve Redirect Loops: Identify and fix redirect loops by ensuring that redirects are configured correctly and do not inadvertently lead back to the original URL.
- Regularly Audit Redirects: Conduct regular audits of redirect configurations to identify and address any issues with redirect chains or loops that may arise over time.
By proactively addressing redirect chains and loops, website owners can ensure a smoother user experience, reduce crawl errors, and maintain optimal SEO performance.
Advanced Strategies and Tips
While basic implementations of 301 redirects are essential for maintaining website integrity and user experience, advanced strategies and tips can further enhance their effectiveness.
Let’s explore advanced techniques such as wildcard redirects, handling parameterized URLs, considering international SEO implications.
And incorporating redirects into marketing strategies to maximize their benefits.
Wildcard Redirects
Wildcard redirects allow webmasters to redirect multiple URLs that match a specific pattern or criteria to a single destination URL.
This advanced technique is particularly useful for managing large-scale URL changes or handling dynamic content structures where individual URL redirects may be impractical.
By defining a wildcard pattern, such as “.example.com/old/“, webmasters can redirect all URLs matching that pattern to a designated destination URL.
This will streamlining the redirect process and ensuring comprehensive coverage of URL changes.
Handling Parameterized URLs
Parameterized URLs contain dynamic query parameters that can vary based on user inputs or other factors, resulting in unique URL variations for the same content.
Handling parameterized URLs effectively requires careful consideration to ensure that all relevant variations are redirected appropriately.
Webmasters can utilize techniques such as URL rewriting, regular expressions, or dynamic redirect scripts to manage parameterized URLs and consolidate link equity effectively.
Webmasters can prevent duplicate content issues and improve SEO performance by redirecting parameterized URLs to canonical versions or implementing URL parameters properly.
International SEO Considerations
Implementing 301 redirects requires additional considerations to ensure that users are directed to the appropriate regional or language-specific versions of the website.
This is particularly crucial for websites targeting international audiences.
International SEO considerations include:
- Implementing hreflang tags to indicate language
- Regional variations of pages
- Setting up geotargeting in Google Search Console
- Using regional subdirectories or subdomains for localized content
Webmasters can enhance user experience, improve search engine visibility, and expand their global reach effectively by incorporating 301 redirects into international SEO strategies.
Incorporating 301 Redirects into Marketing Strategies
Incorporating 301 redirects into marketing strategies can help maximize the impact of promotional campaigns, website redesigns, or product launches.
By strategically redirecting traffic from:
- Promotional URLs
- Campaign landing pages
- Outdated content to relevant, high-converting pages
Marketers can optimize conversion rates, increase engagement, and track campaign performance effectively.
Additionally, utilizing 301 redirects for branded URL shortening, vanity URLs, or affiliate links can enhance brand visibility, improve user experience, and facilitate tracking and analytics.
Businesses can leverage their website’s redirection capabilities to drive traffic, conversions, and brand engagement effectively by integrating 301 redirects into marketing strategies.
Summary of the Topic
- Definition and Purpose: 301 redirects are permanent redirects from one URL to another, serving the purpose of informing browsers and search engines that the requested page has moved permanently.
- Implementation Methods: They can be implemented manually through server configurations like .htaccess files for Apache servers or via plugins/extensions in content management systems like WordPress.
- When to Use 301 Redirects: They are essential during website restructuring, URL changes, handling broken links, or migrating to a new domain or subdomain.
- SEO Implications: 301 redirects play a critical role in preserving link equity, preventing duplicate content issues, and impacting search engine rankings.
- Monitoring and Management: Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure redirects remain effective, address redirect chains and loops, and conduct audits for optimization.
- Advanced Strategies: Wildcard redirects, handling parameterized URLs, considering international SEO implications, and incorporating redirects into marketing strategies are advanced techniques to maximize their benefits.
- Best Practices: Adherence to best practices such as maintaining clean redirect structures, avoiding redirect chains and loops, and regularly auditing and updating redirects ensures optimal performance and preserves SEO integrity.
Implementing 301 redirects effectively is not only essential for maintaining website integrity and user experience but also for preserving SEO equity and maximizing the benefits of website changes or migrations. By understanding the significance of 301 redirects and following best practices, webmasters can ensure seamless navigation, preserve SEO rankings, and enhance overall website performance.